Google released the latest generation of its Operating System, Android 9 Pie back in August last year for Pixel smartphones. The update marked the ninth major release of the software by the company. But, despite the latest generation of Android out almost seven months ago, many of the modern devices are still stuck at one or more generations older software. What’s even more surprising is that some OEMs are launching new smartphones with old software on purpose.

This disparity in Android devices makes the mind think about what problems could there be that restrict some manufacturers into providing older versions of the software. The alarming number of different available Android versions in the market is called Android Fragmentation. This inequality of software versions has plagued the Android Platform since its inception. But is there a way for Google to fix it?
The Current State Of Android Fragmentation

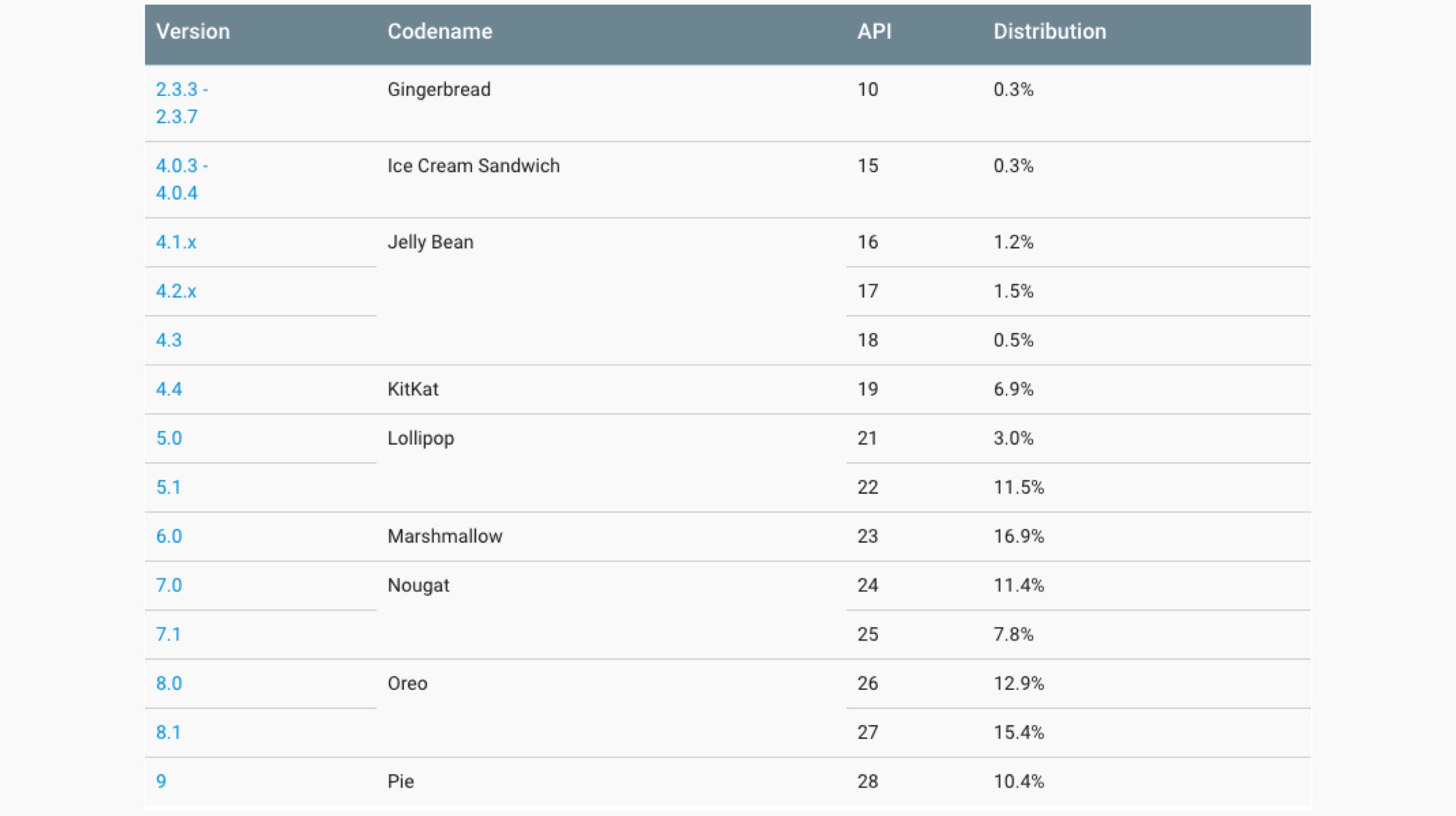
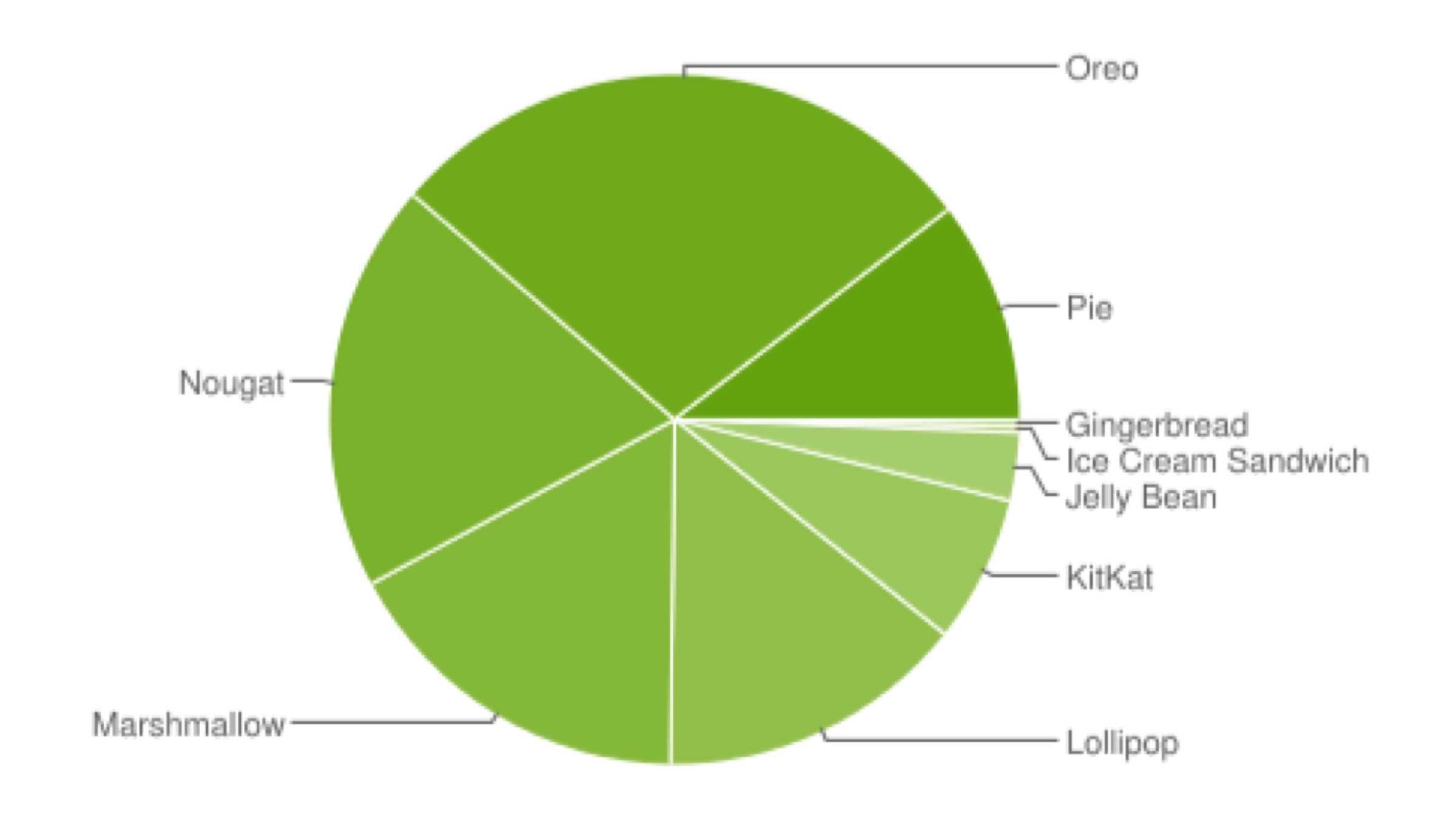
Google releases a report every year in October highlighting the distribution of different software versions. The data, though a few months old, gives an insight on how things are currently on Android’s side. This is what Google found in their testing:
| Version |
Name |
Release Year |
Distribution
(in %)
|
|
2.3.3
2.3.7
|
Gingerbread |
2010 |
0.2% |
|
4.0.3
4.0.4
|
Ice Cream Sandwich |
2011 |
0.3% |
|
4.1
4.2
4.3
|
Jellybean |
2012 |
3.0% |
| 4.4 |
KitKat |
2013 |
7.6% |
|
5.0
5.1
|
Lollipop |
2014 |
17.9% |
| 6.0 |
Marshmallow |
2015 |
21.3% |
|
7.0
7.1
|
Nougat |
2016 |
28.2% |
|
8.0
8.1
|
Oreo |
2017 |
21.5% |
By looking at the above table, there is no mention of the latest Android 9 Pie, because, at the time of this report in October last year, it was still below 0.1%. The numbers are expected to be significantly higher since then. Despite being released for more than two months, the software still couldn’t make it to the list. The most used version was Android 7 Nougat, which had more than 28% of users. This shows how manufacturers refrain from providing any updates to the devices.
Besides not providing new features with the lack of Android updates, they also pose a grave security threat. Every month, Google releases security patches for Android, but not every smartphone gets it. But it’s not the company’s fault, because updating a smartphone with the latest firmware is the OEM’s responsibility.
The Reason For Fragmentation On Android

The reason that the manufacturers continue to provide older software with newer devices or refuse to update them faster than normal; is that most of them have to optimise Android according to the company’s custom skins. These can range from a lightly customised one, like Oneplus’ OxygenOS or a heavily customised take on Android, like Xiaomi’s MIUI. So the OEMs take their own sweet time to adopt the latest version and release it.
When Google provides the manufacturers with the latest Android Platform Development Kit (PDK), they have to start developments on the software. The process includes testing out the new version with the device’s hardware. Then the version is added with manufacturer specific software features, like the aforementioned skin and is tested and certified for bugs. For some manufacturers like HMD Global, Essential and OnePlus, the process has been proven to take only a few days or weeks.
How Can Google Prevent It Further?

The only way that Google can prevent Android Fragmentation from happening in future releases is by being strict with OEMs. And it’s not like the company hasn’t tried. Despite warning the manufacturers when they slacked in providing software updates, the results weren’t much different. Google then released Project Treble in 2017 with Android Oreo. This modified how the updates are delivered by bypassing the chip manufacturers’ modifications to it. It was an ambitious step and worked in theory, but unfortunately, the situation didn’t change much.
Also read: Tesla Unveils Faster Third Generation Supercharger
Google tried to fix Android Fragmentation further by signing up more OEMs to the Android Pie Beta Program. This provided them with more time to develop the software according to their own customisations and was a step in the right direction. But, if the company has to fix the problem further, it has to get more manufacturers on board and if possible, then all of them. But this sends out hope that the company is serious about the issue and it may take some more time to fix. If manufacturers are serious about the disparity in updates, the days of Android Fragmentation may be over sooner than later.