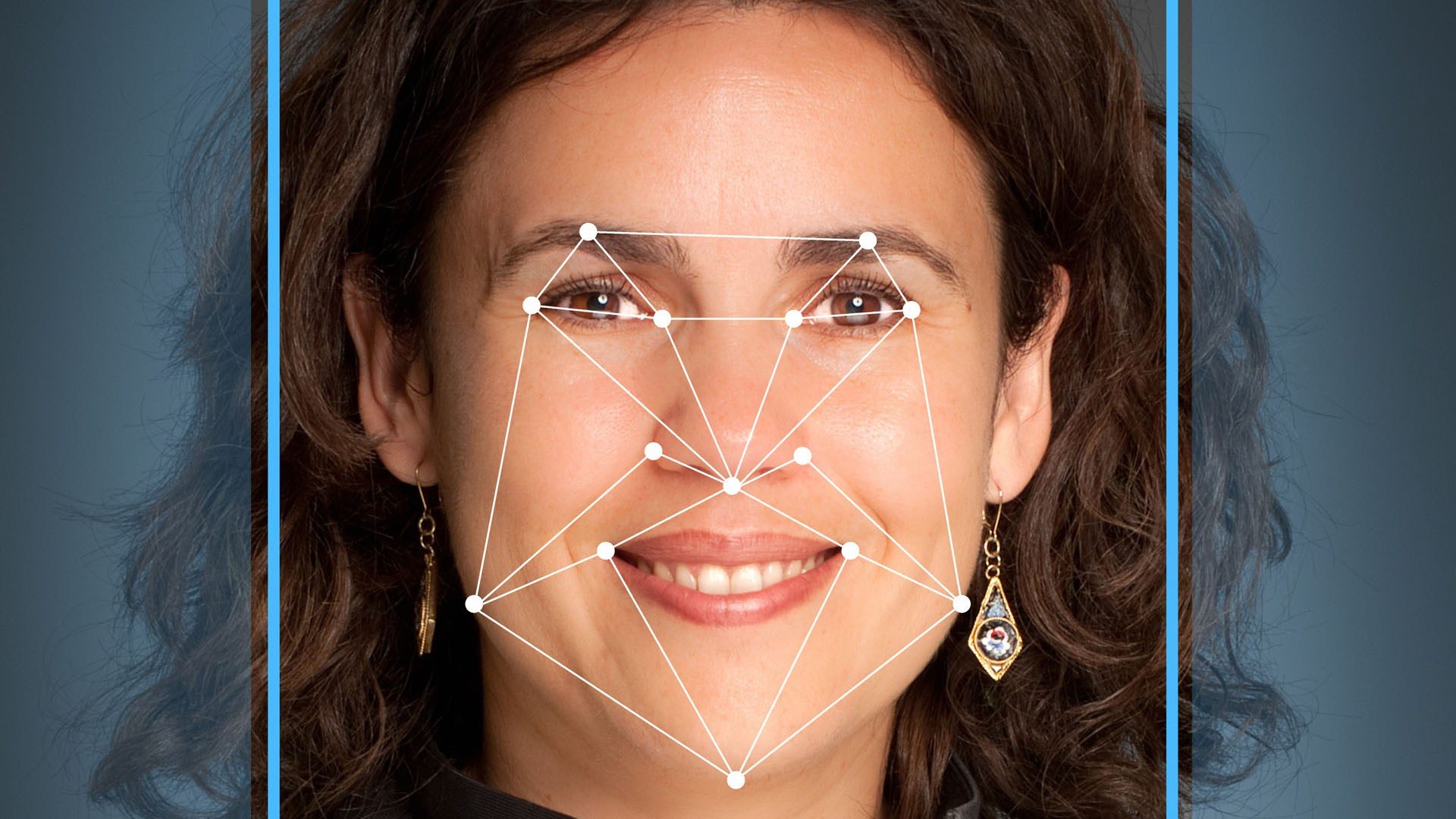
As a consequence to yet another accusation, American technology giant Microsoft quietly removed an online database that contained a whopping 10 million images of almost 1,00,000 people. As per reports, the images were derived from a multitude of search engines and were published in a dataset called MS Celeb in the year 2016. Accusations stated that many people in the dataset were not aware that their images were being used and that their consent wasn’t asked for while capturing the images.

The images in the Microsoft dataset were being used to train AI based facial recognition systems around the world. For instance, Chinese firms SenseTime and Megvii were using the images in the set to develop their software. Moreover, military researchers were also making use of the images to train recognition-based applications. The same dataset was previously used in an AI project to identify various celebrities. Sources state that the database has been directly linked to China’s efforts to crack down on ethnic minorities in the country.
The images of people included in Microsoft’s database were scraped from the web under the Creative Commons License. As per the License, people can academically reuse the images, provided that permission has been granted by the copyright holder of the image, not the subject of the image. Previously, in April 2019, the Chinese government used facial recognition software to keep tabs on 11 million Uighurs (Muslim Minority).
Also Read: NASA Opens Commercial Opportunities For The International Space Station
This may be an alarming wake-up call for conglomerates in the light of the fact that consent is absolutely compulsory. If a check is not kept on the method which is being implemented to capture facial-recognition data, the same data can be used in unethical ways. Law enforcement agencies these days rely heavily on technology to ease investigations, but any software isn’t without its flaws. Further developments will expectedly shine more light on the case, but as of now, Microsoft has not stated anything regarding the matter.