Samsung today announced its Heterogeneous Multi-Processing (HMP) solution for the Exynos 5 Octa to fully maximize the benefits of the ARM big.LITTLE technology. The HMP capability gives system-level designers the ability to develop solutions that might deliver the right combination of high-performance and low-power to carry out tasks like 3D gaming, complex augmented reality and advanced web browsing.
It’s usually assumed that the big CPU will do all the performance-critical work, however, power-efficient little cores can handle many significant workloads all on their own, so the workload is balanced within the system,” said Taehoon Kim, vice president of System LSI marketing, Samsung Electronics. “big.LITTLE processing is designed to deliver the right combination of processors for a specific job. An eight-core processor with HMP is the truest form of the big.LITTLE technology with limitless benefits to the users of high-performance, low-power mobile products.”

This technology will be available in the 4th quarter of this year, it will let devices access both sides of the big.LITTLE ARM configuration simultaneously, which the company claims will increase both performance and efficiency. While software threads with high priority use the “big” A15 core, lower priority tasks can run on the “small” A7 without needing to switch back and forth, says Samsung. Samsung isn’t the only one running this setup, as MediaTek also announced an improvement for its MT8135 back in July.
ARM big.LITTLE multi-processing technology delivers the highest performance and efficiency across the widest range of workloads,” said Noel Hurley, vice president, Strategy and Marketing, Processor Division, ARM. “We welcome Samsung’s continued commitment to deploying the leading-edge technology on their latest chips featuring the ARM Cortex™-A series of processors, ARM Mali™ GPUs and ARM Artisan™ physical IP.”
The video below shows, the Samsung Exynos 5 Octa has eight core processor, four little ones for small always on application, and four bigger application for graphic intensives stuff.
[youtube id=”Zwbeb08W27U” width=”100%” height=”300px”]
[toggle title=”Press Release “]Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., a world leader in advanced semiconductor solutions, today announced its Heterogeneous Multi-Processing (HMP) solution for the Exynos 5 Octa to fully maximize the benefits of the ARM® big.LITTLE™ technology. The HMP capability gives system-level designers the ability to develop solutions that deliver the right combination of high-performance and low-power to carry out tasks such as 3D gaming, complex augmented reality and advanced web browsing.
“It’s usually assumed that the big CPU will do all the performance-critical work, however, power-efficient little cores can handle many significant workloads all on their own, so the workload is balanced within the system,” said Taehoon Kim, vice president of System LSI marketing, Samsung Electronics. “big.LITTLE processing is designed to deliver the right combination of processors for a specific job. An eight-core processor with HMP is the truest form of the big.LITTLE technology with limitless benefits to the users of high-performance, low-power mobile products.”
“ARM big.LITTLE multi-processing technology delivers the highest performance and efficiency across the widest range of workloads,” said Noel Hurley, vice president, Strategy and Marketing, Processor Division, ARM. “We welcome Samsung’s continued commitment to deploying the leading-edge technology on their latest chips featuring the ARM Cortex™-A series of processors, ARM Mali™ GPUs and ARM Artisan™ physical IP.”
HMP is the most powerful use model for ARM big.LITTLE technology, as it enables the use of all physical cores at the same time. Software threads with high priority or high computational intensity can be allocated to the ‘big’ Cortex-A15 cores while threads with less priority or are less computationally intensive, can be performed by the ‘LITTLE’ Cortex-A7 cores, enabling a highly responsive, low-energy system to be built.
Software implementation is essential to maximizing the benefits of big.LITTLE technology. Multi-processing software controls the scheduling of threads of execution to the appropriate core. In earlier versions of the big.LITTLE software, the whole processor context is moved up to the ‘big’ core or down to the ‘LITTLE’ core based on the measured work load. In-depth study and analysis of diverse use case scenarios enable Samsung to achieve efficiency and high-performance, while managing power levels to deliver optimal user environments.
The HMP solution for Samsung’s Exynos 5 Octa application processors will be available to customers in 4Q of 2013.
About Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. is a global leader in technology, opening new possibilities for people everywhere. Through relentless innovation and discovery, we are transforming the worlds of televisions, smartphones, personal computers, printers, cameras, home appliances, LTE systems, medical devices, semiconductors and LED solutions. We employ 236,000 people across 79 countries with annual sales exceeding US$187.8 billion. To discover more, please visit www.samsung.com.
[/toggle]









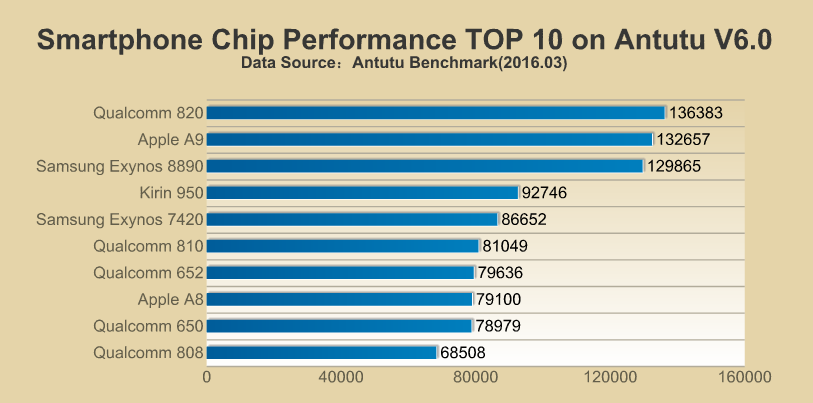
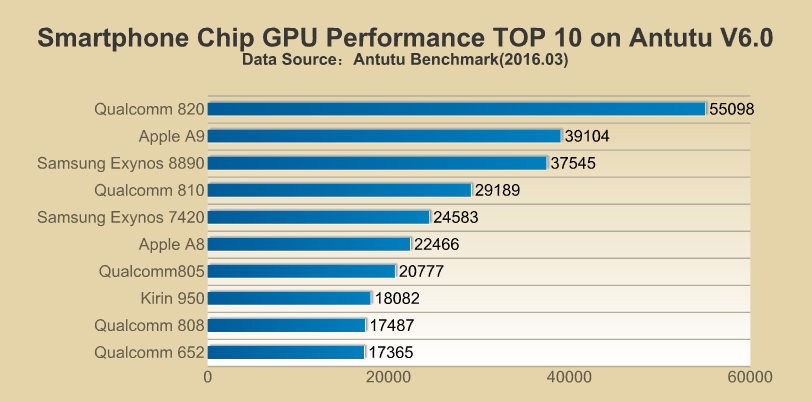










 But from this partnership, Apple’s former partners like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) and Sandisk may get a significant blow. TSMC used to manufacture chips for all the previous models of the iPhone and SanDisk was given the responsibility of memory chips for iPhone, iPad and Mac.
But from this partnership, Apple’s former partners like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) and Sandisk may get a significant blow. TSMC used to manufacture chips for all the previous models of the iPhone and SanDisk was given the responsibility of memory chips for iPhone, iPad and Mac.


