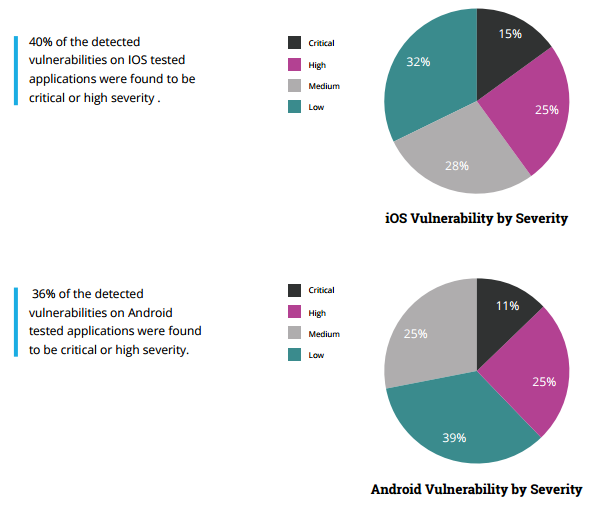
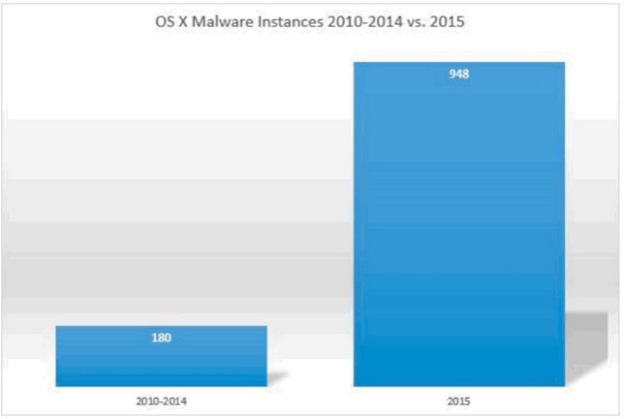
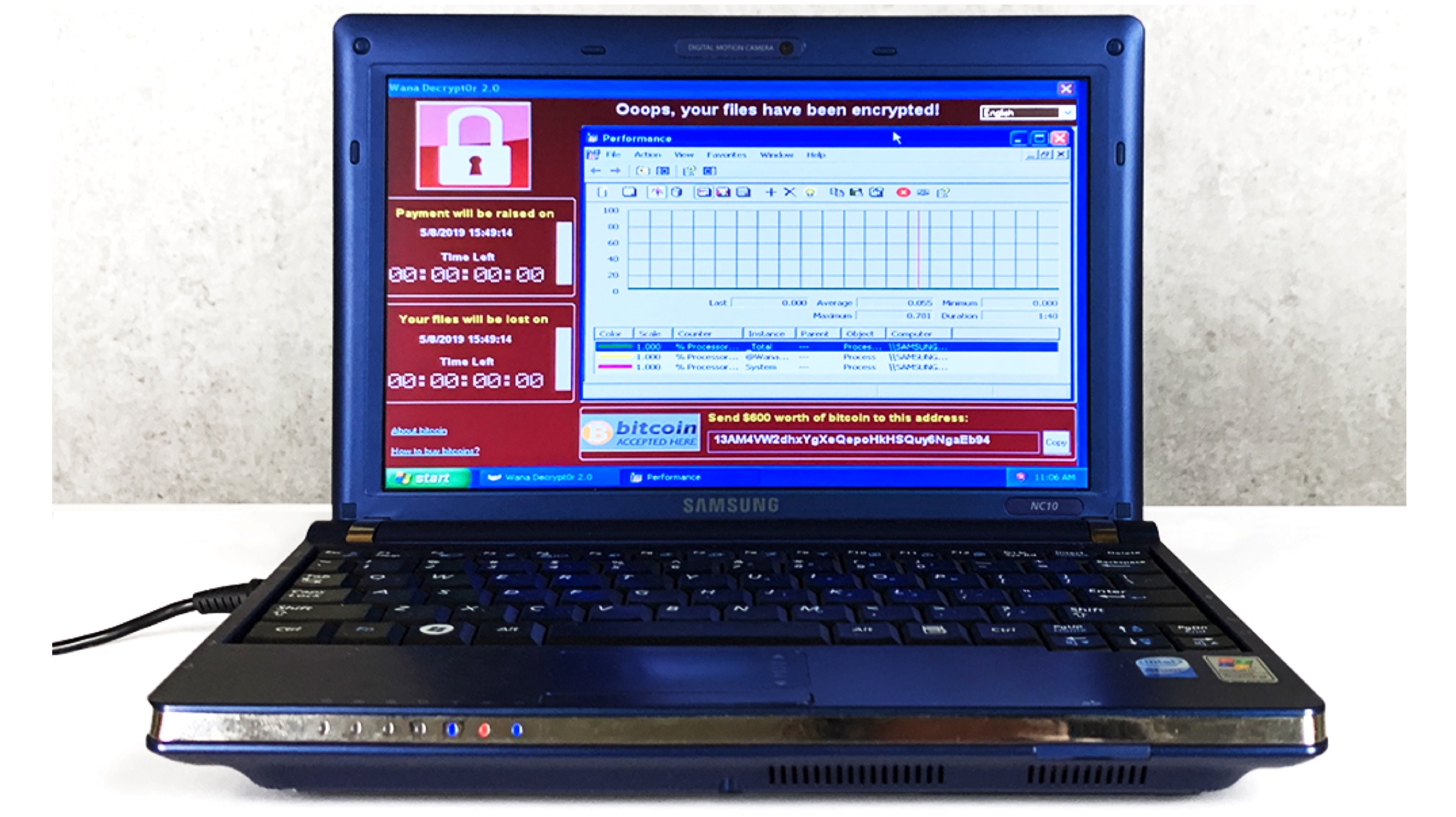
Apple released its routine iOS 12.4 update for iPhones and iPads earlier this month. The update, like most software updates by the company claims of patching newly found security flaws and bugs. Now, in the latest report, it has been revealed that most of these serious security flaws that were patched in the iOS 12.4 update were originally discovered by Google security researchers. Out of the total six bugs reported, five have been already fixed, with one unknown flaw still remaining unchecked.
About The Security Flaws

The aforementioned security flaws in the latest version of iOS were found by two members of Google’s Project Zero bug-hunting team. These two people are named Natalie Silvanovich and Samuel Groß, who alerted Apple immediately upon finding the flaws. While what vulnerabilities were discovered have not been revealed for obvious security purposes, they have been claimed to be interactionless. This means they can be exploited without any interaction from the user of the iPhone. The flaw has been found in the smartphone’s iMessage application.

Among the total six security flaws found by Google, at least four relied on the attacker/hacker sending malicious code to an iPhone. It is recommended that users of the Apple iPhone who still have not updated their device, do so at the earliest. The remaining security flaw that still hasn’t been patched, is expected to be fixed with the next update of the iOS software.
What Is Project Zero?
![]()
Also read: The Samsung Galaxy M20s Will Feature a Massive 5830 mAh Battery
Project Zero is a team of security analysts that are employed by Google. The team is aimed at finding zero-day vulnerabilities; that is bugs in software before they are found by anyone else for malicious use. These vulnerabilities, if left unchecked can be exploited by various criminal organisations, hackers and many intelligence agencies. Project Zero was announced by Google on the 15th of July 2014 and has been responsible for finding many serious security flaws with major software and devices.

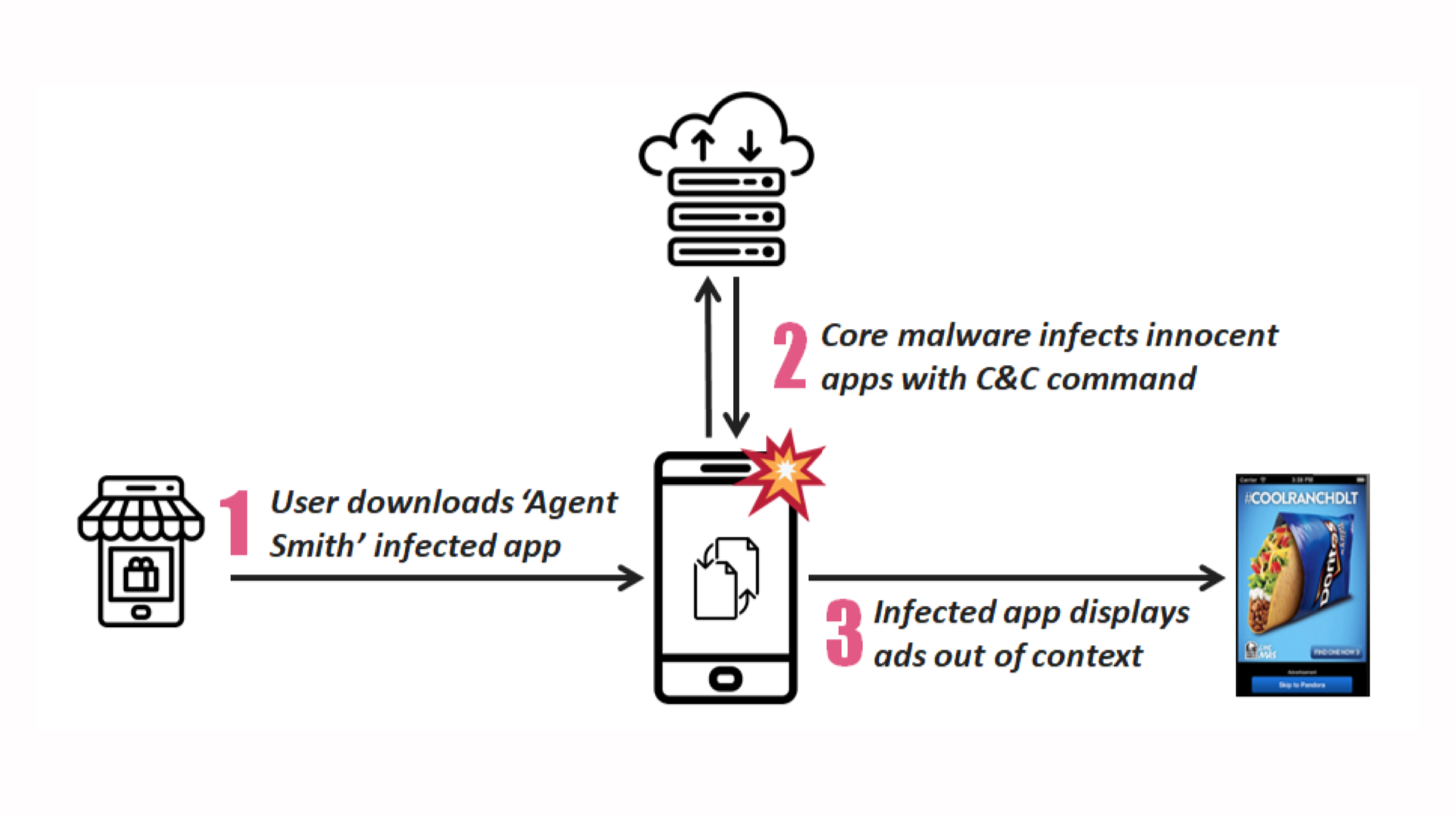
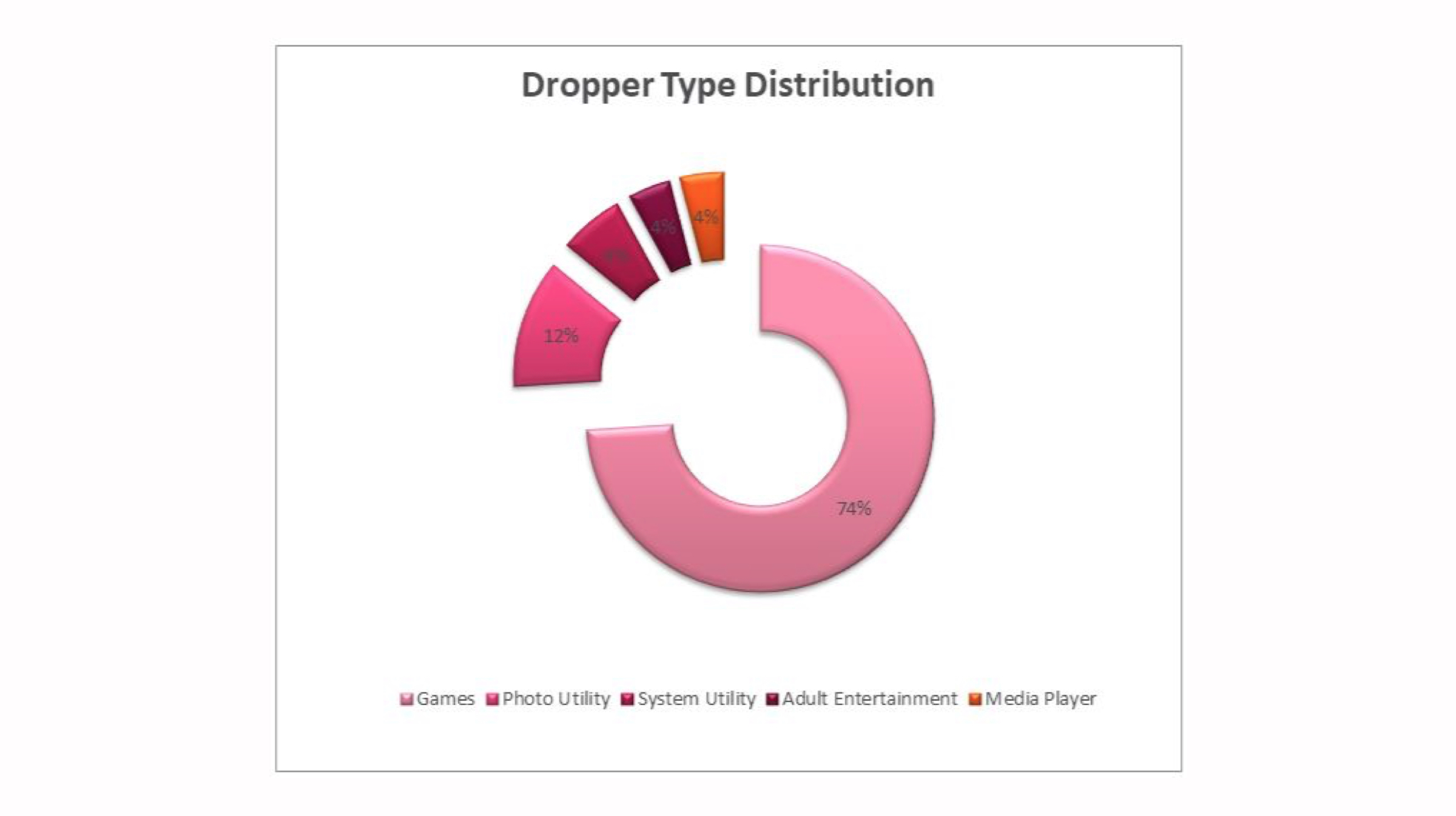
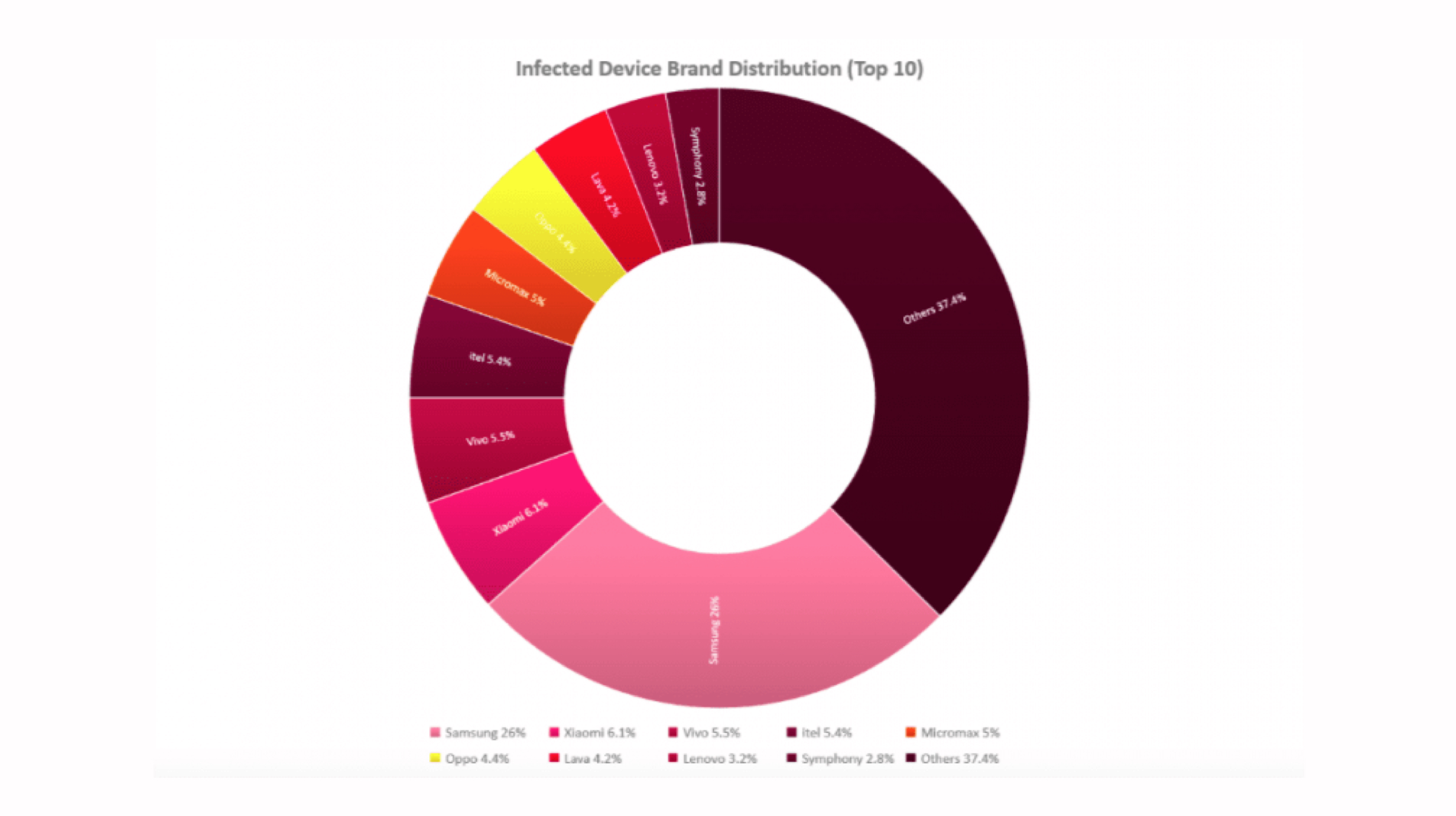








 As reported, several apps which are downloaded from the Play Store tend to display objectionable links and content on their screens. The links and clickable content then redirects the users to ‘scam’ websites, where information is misused. Supposedly, these ‘fake’ apps can access remote ad configuration servers for performing their phishing attacks. Previously, Google banned some Crypto-mining apps from their Play Store, due to policy changes by Google in July 2018. It also banned Chrome crypto-mining apps from the Chrome store. Crypto-jacking was a pretty common activity at that time. Hackers used to take over user’s devices for crypto-mining, even on mobile devices.
As reported, several apps which are downloaded from the Play Store tend to display objectionable links and content on their screens. The links and clickable content then redirects the users to ‘scam’ websites, where information is misused. Supposedly, these ‘fake’ apps can access remote ad configuration servers for performing their phishing attacks. Previously, Google banned some Crypto-mining apps from their Play Store, due to policy changes by Google in July 2018. It also banned Chrome crypto-mining apps from the Chrome store. Crypto-jacking was a pretty common activity at that time. Hackers used to take over user’s devices for crypto-mining, even on mobile devices. Also Read :
Also Read :