In an era where security is the defining factor of our lives, people are becoming increasingly aware of their privacy across digital devices as well. Hacking incidents have increased, which is indirectly putting pressure on smartphone companies to incorporate the highest level of security detail in their devices. A major chunk of all smartphones being launched these days have a common biometric security feature: the fingerprint scanner. But the real question is, how accurate and effective are those fingerprint scanners in reality? Are they secure enough to just prevent snooping, or are they built for something more resilient?
Types Of Scanners, And How Do They Work?
 These days, smartphones are loaded with a host of security options to ensure that the data on the device remains private to the user. Some primary security features are listed below:
These days, smartphones are loaded with a host of security options to ensure that the data on the device remains private to the user. Some primary security features are listed below:
- Pattern
- PIN/Password
- Fingerprint Scanners
- Iris/Retina Scan
- Face Recognition
Pattern and password enabled security has been around since almost the beginning of the smartphone era, and most of the users are familiar with it. A few years ago, fingerprint scanning was considered to be something that belonged only to spy movies. Fingerprint scanners were a state-of-an-art technology back then. But in the past few years, fingerprint scanners have become a ubiquitous part of our technology. They are extremely useful because of the ease in their implementation. But how do fingerprint scanners work?
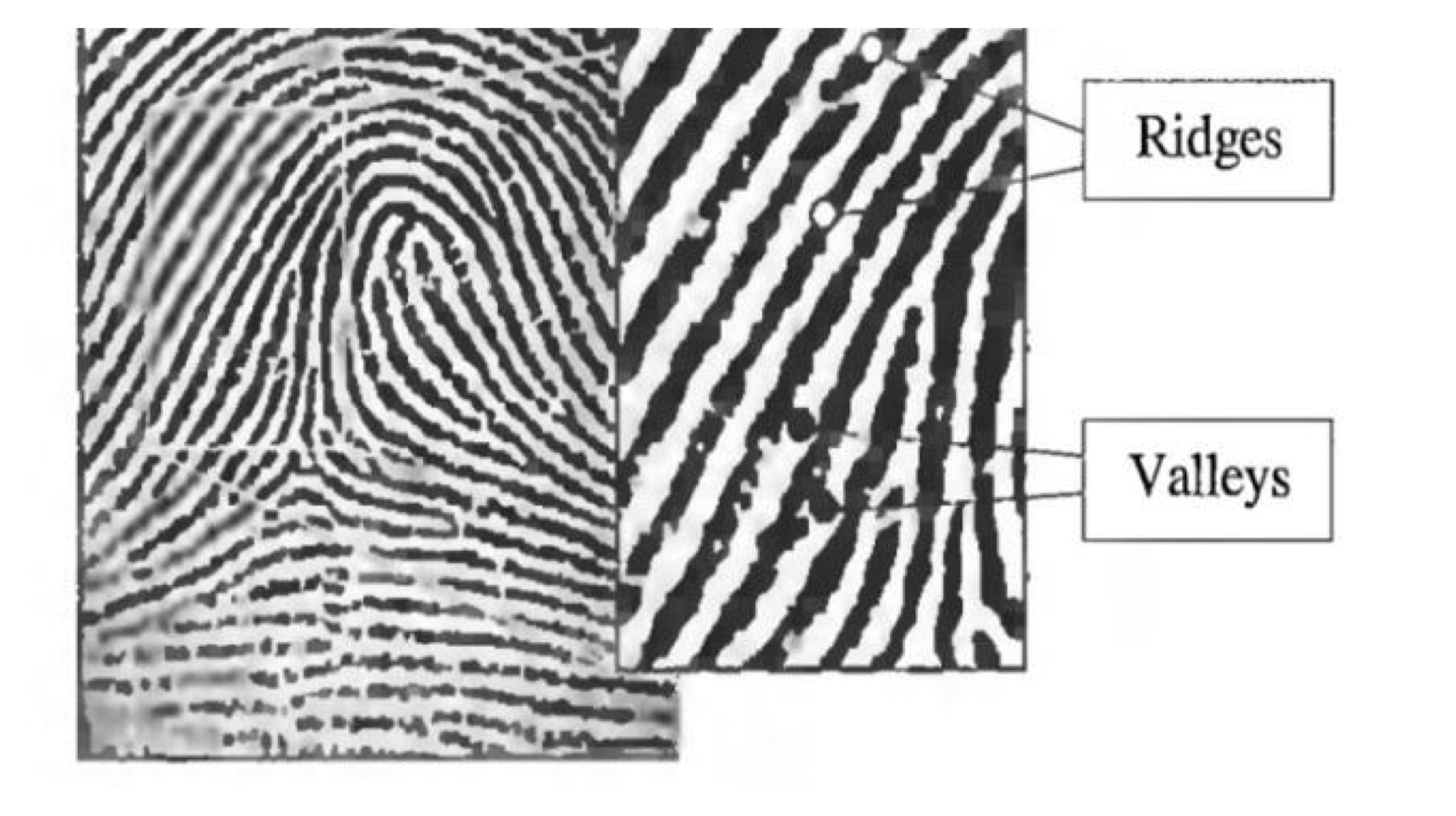
Every human fingerprint consists of two main physical contours. The raised parts of the finger are called the ridges, whereas the areas between the ridges are referred to as the valleys. When a user places his finger on the scanner, the CCD (Charged Coupled Device) light sensor generates an inverted image of the finger using its own light source. The LEDs generate enough light to illuminate the ridges of the finger. The image generated by the CCD sensor is actually a two toned image. The darker areas represent the ridges of the finger, while the lighter areas represent the valleys between the ridges.
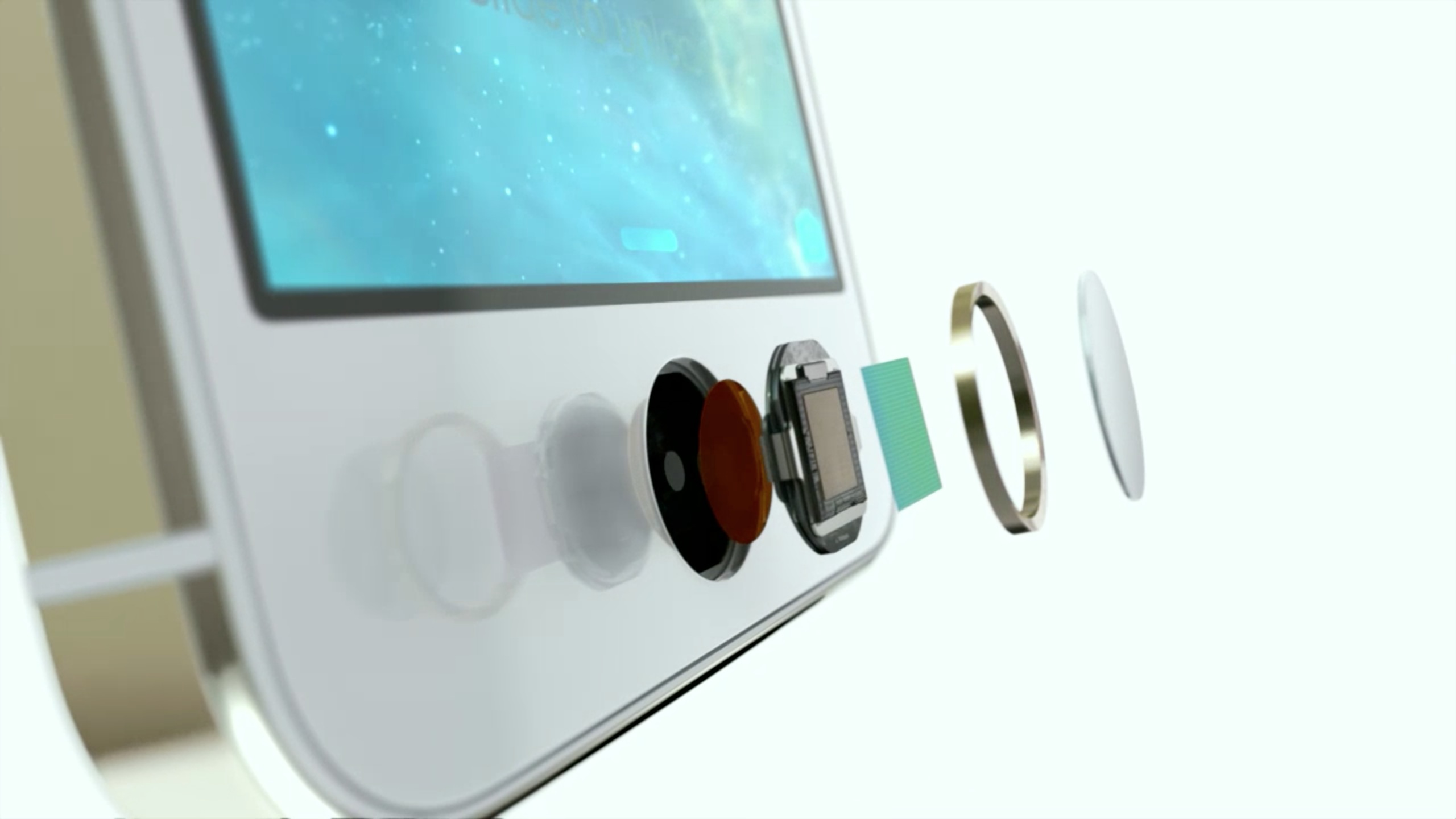 The processor in the scanner module ensures that the image generated is clear enough to process. In addition, the processor also checks the pixel darkness. If the image is too dark or too light, it is discarded. The scanner then adjusts the exposure time of the sensor and scans the fingerprint again. As soon as a crisp image is generated, the fingerprint is cross checked with other images/prints of the finger. Every fingerprint signature is entirely unique, so any print that matches any other image in the list is picked as the verifiable one.
The processor in the scanner module ensures that the image generated is clear enough to process. In addition, the processor also checks the pixel darkness. If the image is too dark or too light, it is discarded. The scanner then adjusts the exposure time of the sensor and scans the fingerprint again. As soon as a crisp image is generated, the fingerprint is cross checked with other images/prints of the finger. Every fingerprint signature is entirely unique, so any print that matches any other image in the list is picked as the verifiable one.
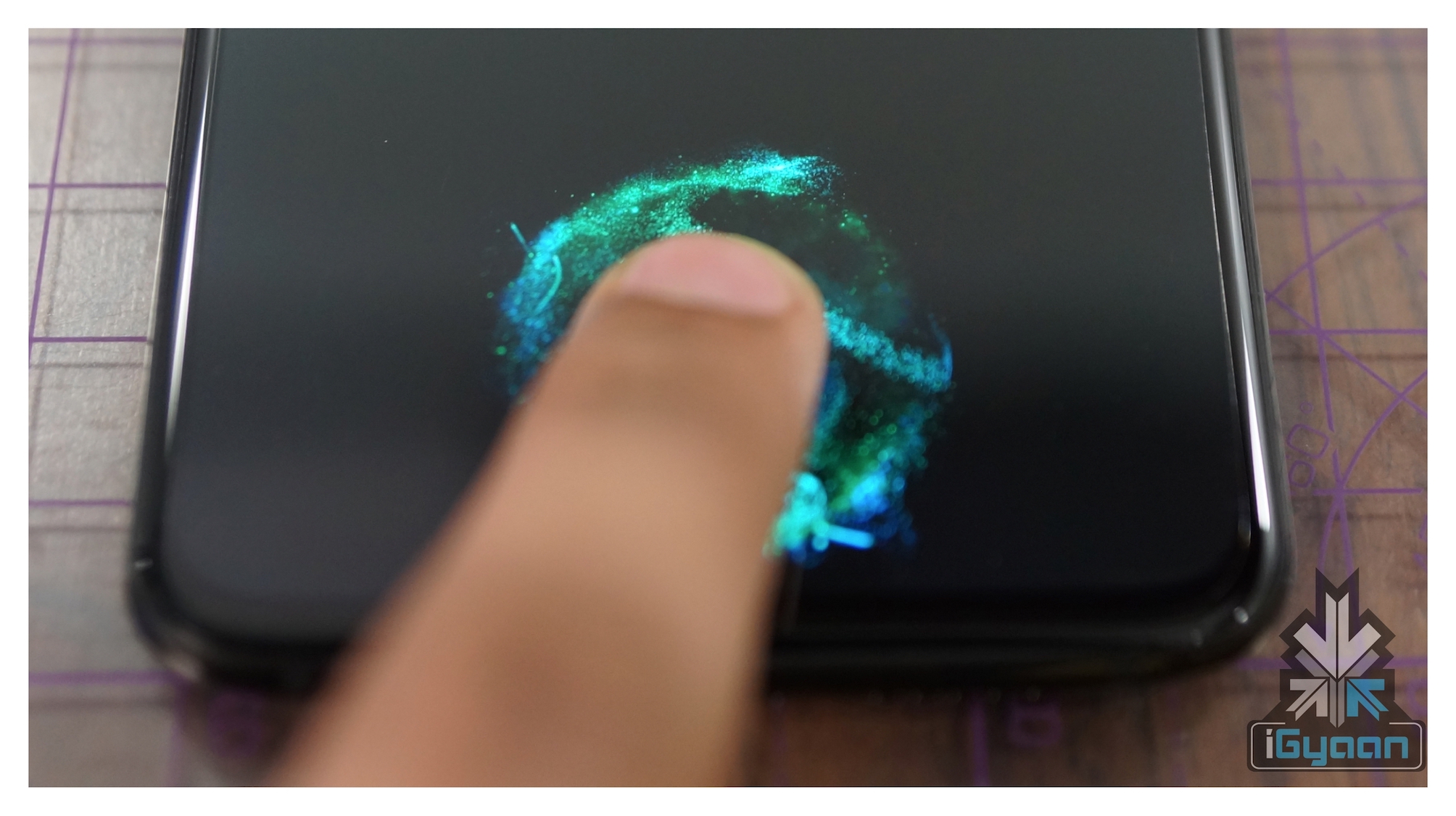 Unlike Digital Scanners, Capacitive scanners make use of electrical current to verify fingerprints. The capacitive sensors are made of semiconductor chips. Each chip contains a small array of cells with conductor plates, which in turn are covered by an insulating material. When the finger is placed on a capacitive scanner, the finger’s image is developed by the process of varying input and output voltage.
Unlike Digital Scanners, Capacitive scanners make use of electrical current to verify fingerprints. The capacitive sensors are made of semiconductor chips. Each chip contains a small array of cells with conductor plates, which in turn are covered by an insulating material. When the finger is placed on a capacitive scanner, the finger’s image is developed by the process of varying input and output voltage.
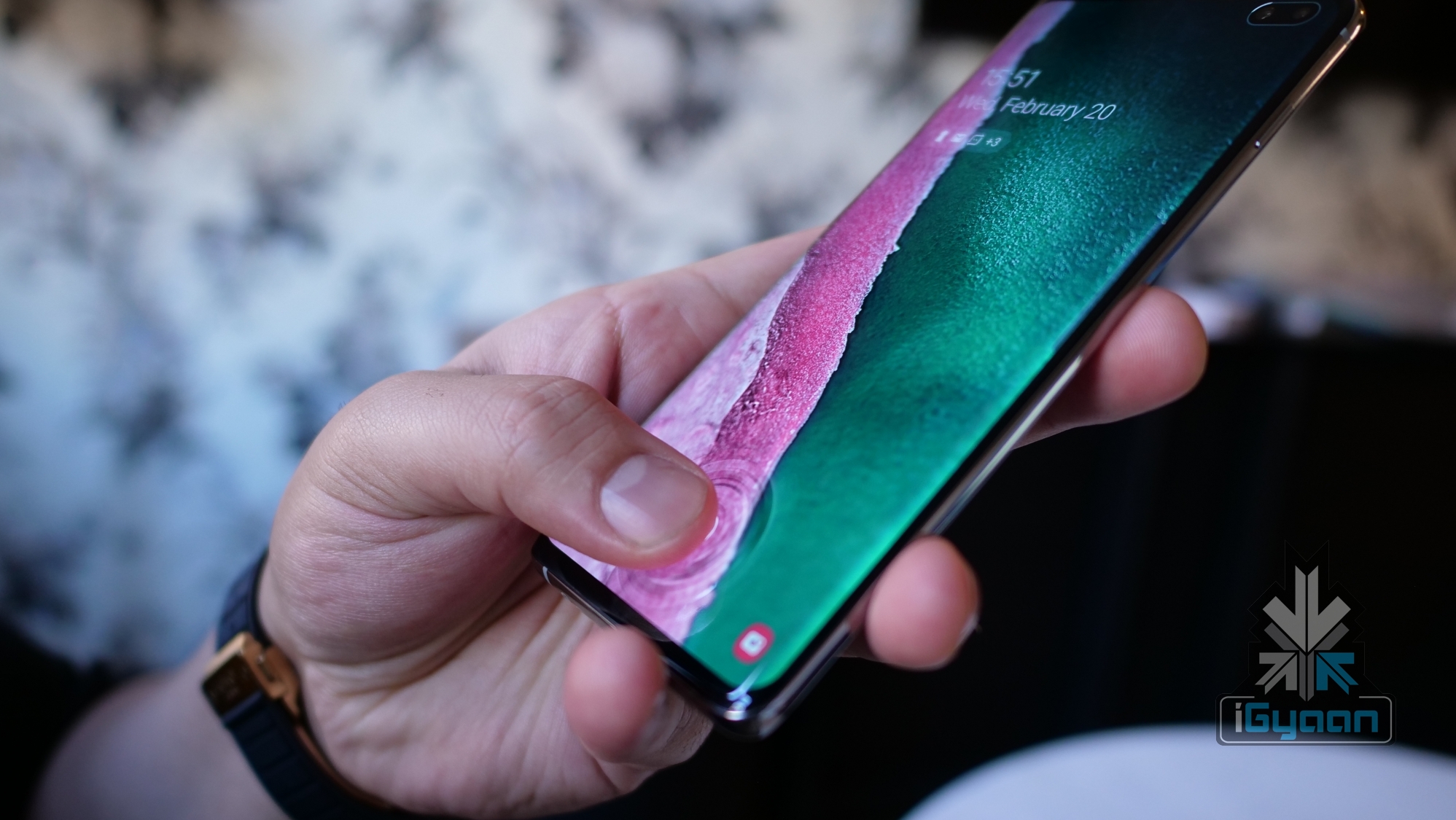 Ultrasonic Scanners are fairly recent. Samsung’s latest S10 series smartphones are the first ones to sport ultrasonic fingerprint sensors in the market. An ultrasonic pulse is transmitted via the screen to the user’s finger, which reciprocates the ridges, pores and valleys in the finger to create a much more accurate 3D fingerprint image.
Ultrasonic Scanners are fairly recent. Samsung’s latest S10 series smartphones are the first ones to sport ultrasonic fingerprint sensors in the market. An ultrasonic pulse is transmitted via the screen to the user’s finger, which reciprocates the ridges, pores and valleys in the finger to create a much more accurate 3D fingerprint image.
Security Concerns Regarding Fingerprint Scanners
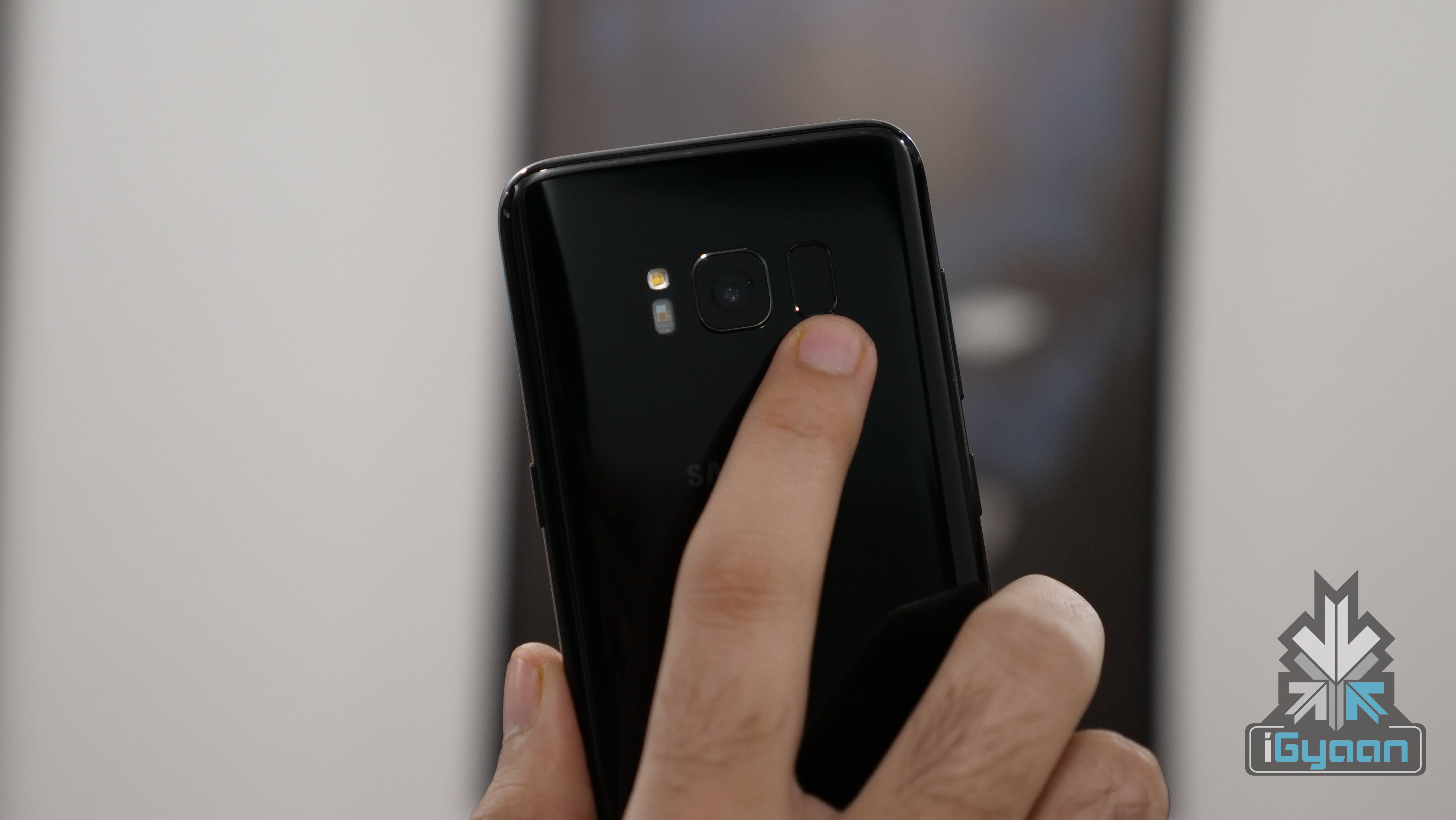

Someone who knows how the fingerprint scanner works can also design fairly simple methods of bypassing its security detail. For instance, the fingerprint scanner can be fooled with the help of a dental mold cast. After filling the cast with some playing clay, the only thing left is to get the owner of the phone to touch the material. Of course, this requires the help of the person who owns the device, but in retrospect, a person leaves his fingerprint as a residue on multiple objects of daily use which can be used for the same purpose.
If a person has a 3D printer and a single high resolution image of the owner’s finger, a 3D printed mold can be created which can then be used to unlock the device. Some may argue that in such a case, PINs, passwords, and patterns are more secure, but unless you are a highly valued individual with sensitive information stored on your phone, you don’t need to worry about people hard-hacking into your phone via the fingerprint sensor, as the process takes some time and discretion.
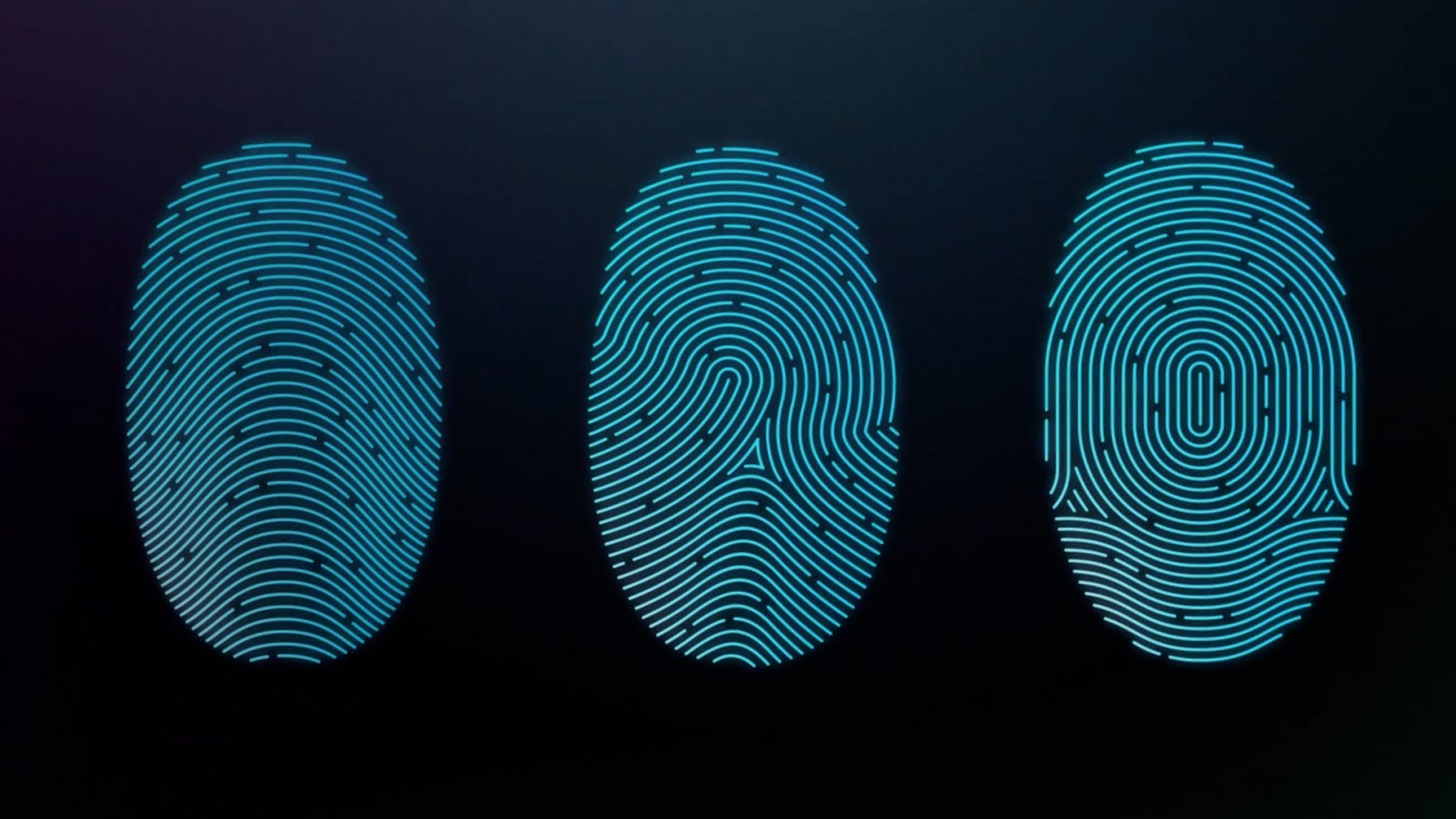 Full fingerprints are extremely difficult to fake, but instead, the smartphone fingerprint scanners only record partial fingerprint signatures. Findings indicate that if a person creates a glove with a masterprint (with the highest possible number of ridge-and-valley combinations), he/she can break into a fingerprint protected device 40 to 50 percent of times before the smartphone asks for a numeric PIN. And that’s a scary high probability of something like this happening in our daily life, again, highly unlikely.
Full fingerprints are extremely difficult to fake, but instead, the smartphone fingerprint scanners only record partial fingerprint signatures. Findings indicate that if a person creates a glove with a masterprint (with the highest possible number of ridge-and-valley combinations), he/she can break into a fingerprint protected device 40 to 50 percent of times before the smartphone asks for a numeric PIN. And that’s a scary high probability of something like this happening in our daily life, again, highly unlikely.
Conclusion
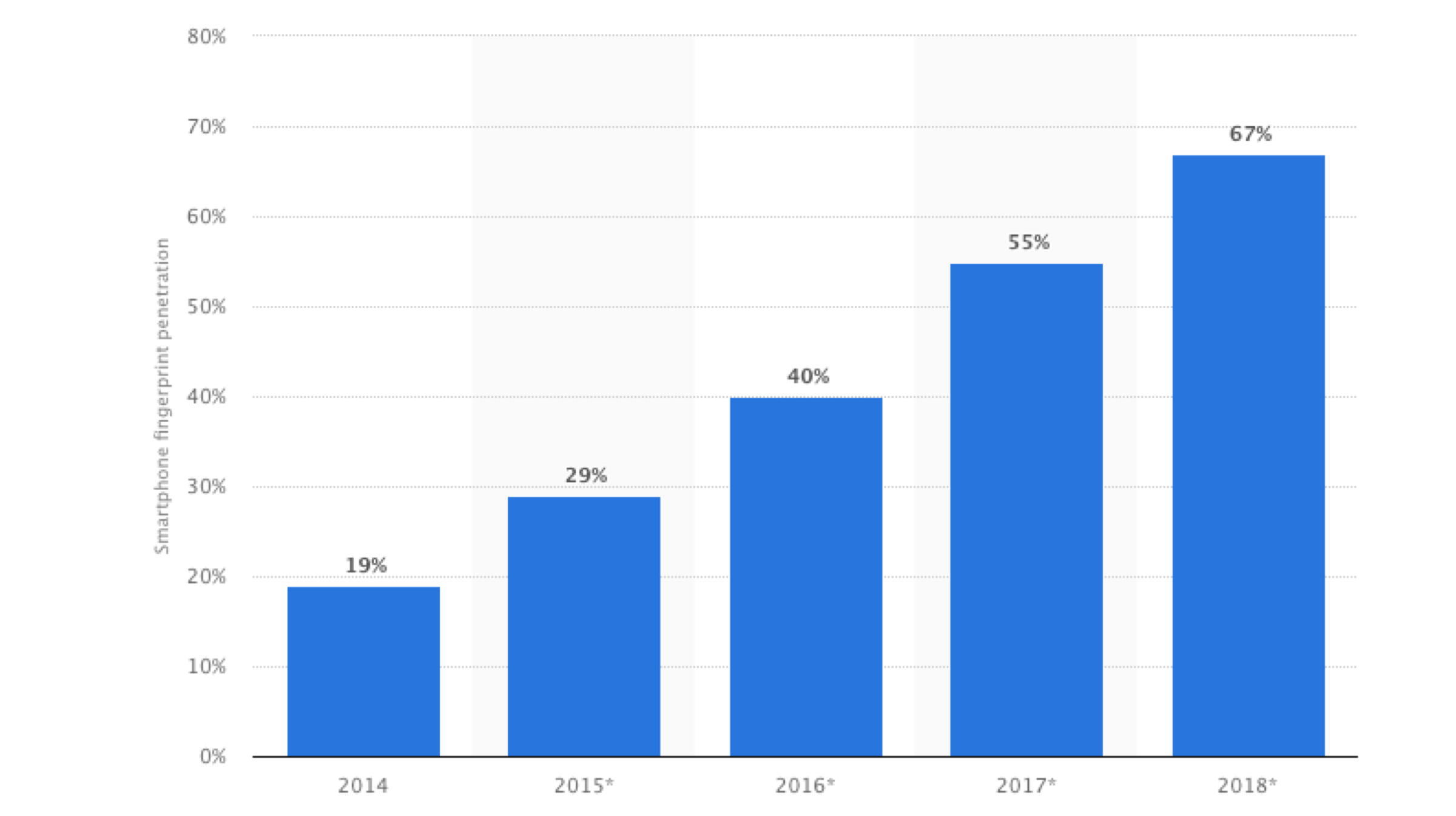
Also Read: Apple Told To Pay Qualcomm Over $31 Million In Patent Infringement Case
The graph above clearly depicts the increasing penetration of fingerprint scanners in the smartphone market by 2018. So it’s clear that the market is not getting rid of fingerprint scanners anytime soon. When it comes to solutions, the most “implementation-worthy” idea is to include a significantly larger fingerprint sensor which will increase the signature accuracy of the finger. Also, users should abstain from using fingerprint sensors while transferring large amounts of money or authenticating sensitive applications. Foolproof ways of biometric authentication are still being tested out, so eventually, we’ll get where maximum security can be achieved.


![]()






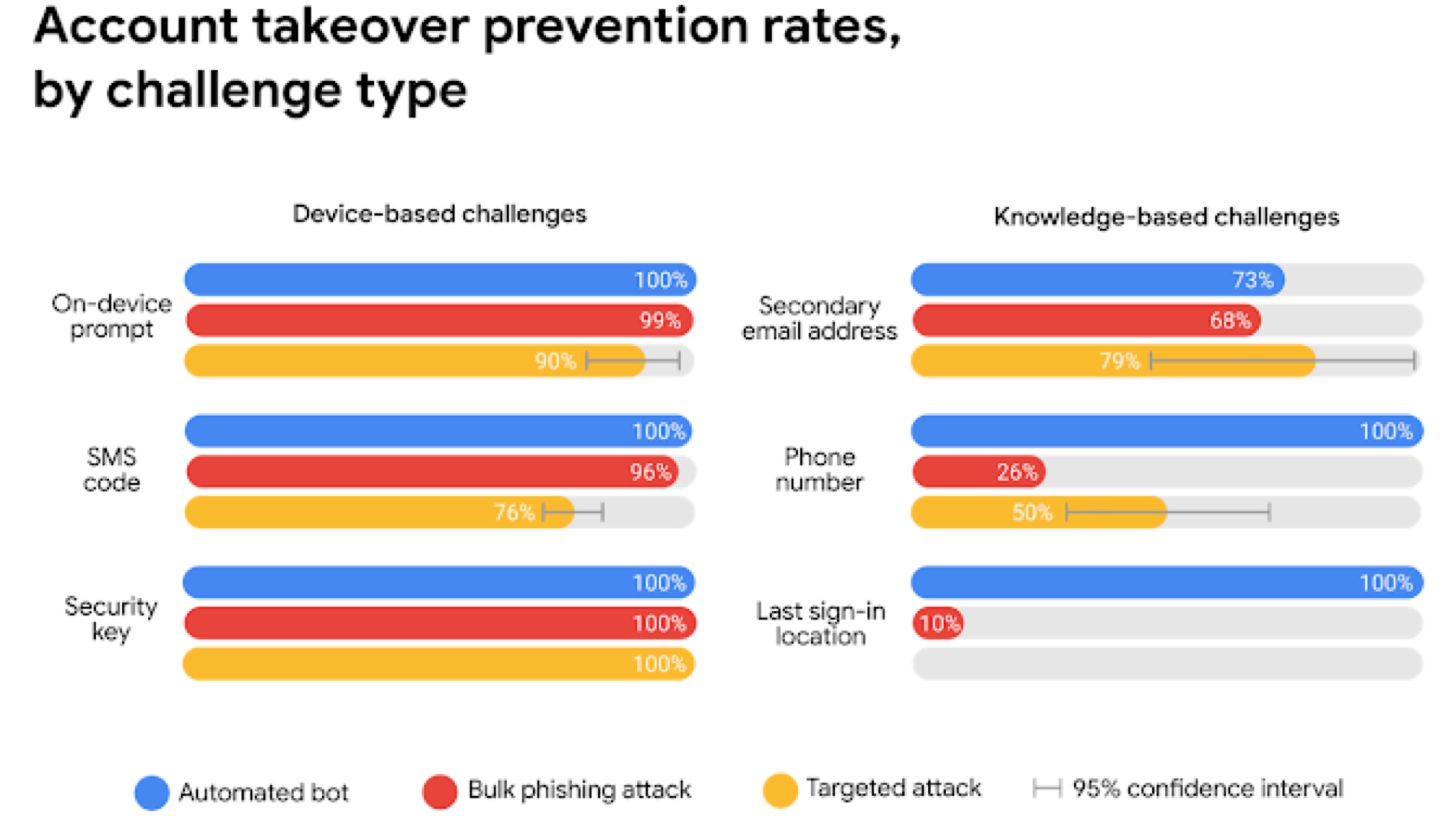 The year long study on security attacks was presented by the company at a gathering of experts and policy-makers, called the Web conference. Google’s research stated that adding a recovery phone number can block up to 100% of all automated bots, 99% of all bulk phishing attacks and 66% of targeted security attacks. This study was carried out with researchers from New York University and the University of California, San Diego primarily to highlight how basic “account hygiene” can keep accounts safe.
The year long study on security attacks was presented by the company at a gathering of experts and policy-makers, called the Web conference. Google’s research stated that adding a recovery phone number can block up to 100% of all automated bots, 99% of all bulk phishing attacks and 66% of targeted security attacks. This study was carried out with researchers from New York University and the University of California, San Diego primarily to highlight how basic “account hygiene” can keep accounts safe.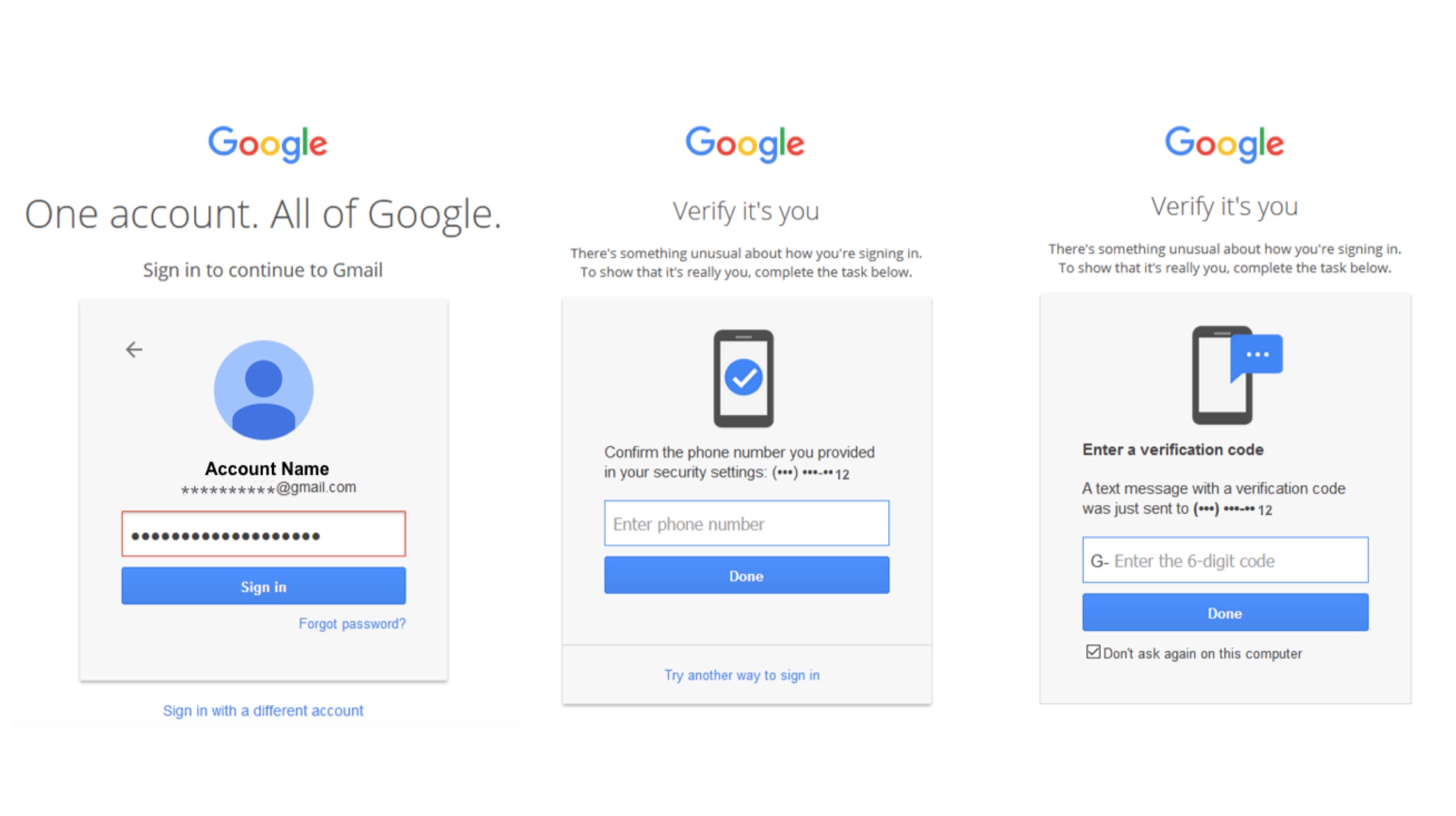 Also Read:
Also Read: 





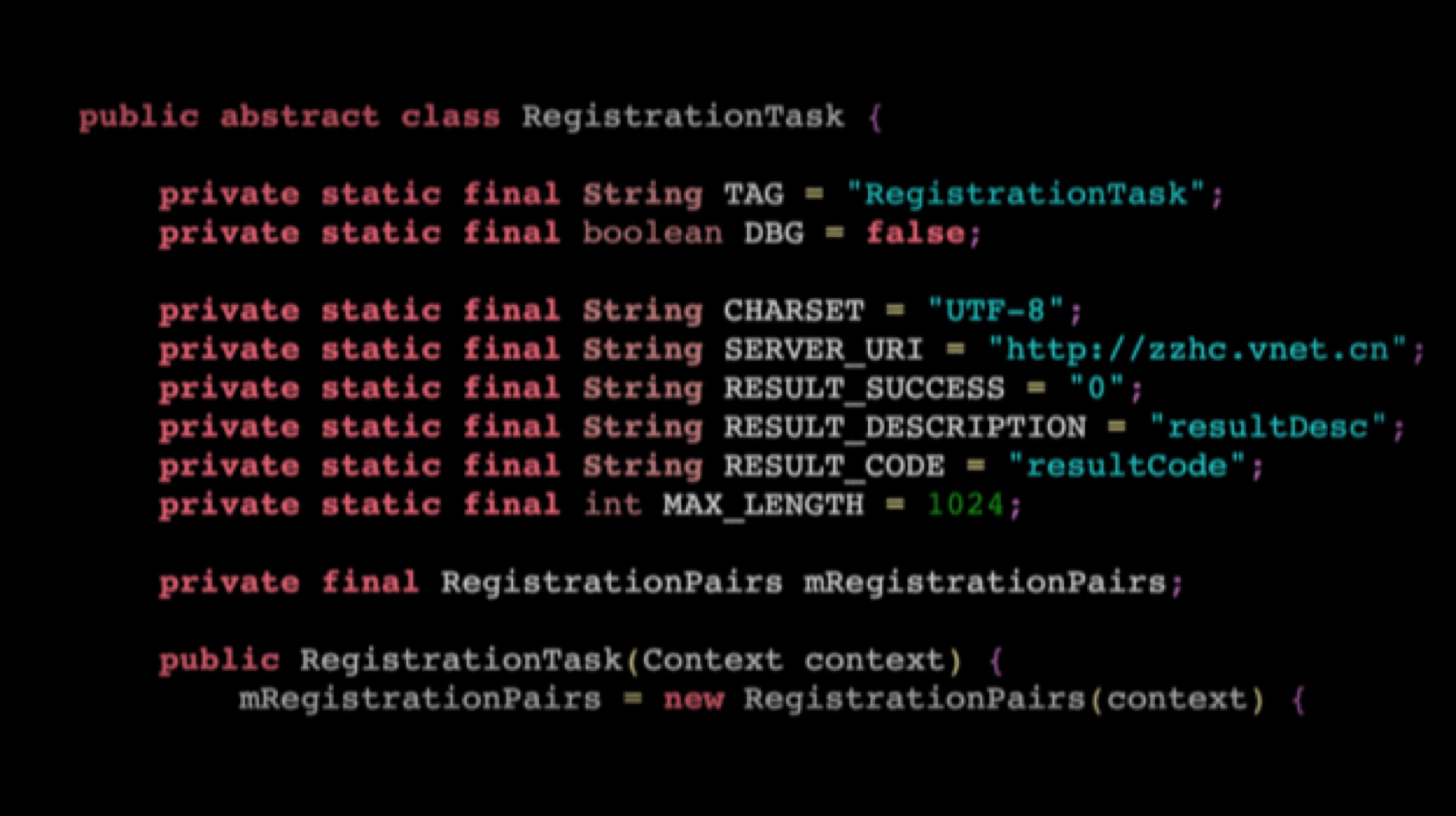 The Finnish company had mistakenly installed the Chinese device activation client on the Nokia smartphones which were intended to retail outside China. Consequently, the activation data was being sent to vnet.cn, a Chinese server located in the China Internet Network Information Center, or CNNIC. The domain is owned by the state-run Chinese Telecom operator.
The Finnish company had mistakenly installed the Chinese device activation client on the Nokia smartphones which were intended to retail outside China. Consequently, the activation data was being sent to vnet.cn, a Chinese server located in the China Internet Network Information Center, or CNNIC. The domain is owned by the state-run Chinese Telecom operator. HMD Global also stated that the issue was taken care of in the month of February since most Nokia 7 Plus smartphones had been updated with the bug fix. Users can check if the fix is installed in their devices by going to Settings>System>About Phone>Build Number. The build number should be “00WW_3_39B_SP03” or “00WW_3_22C_SP05“. If the build number does not match, users may need to update their device. This can be done by going to Settings> System> Advanced>System Update>Check for Update.
HMD Global also stated that the issue was taken care of in the month of February since most Nokia 7 Plus smartphones had been updated with the bug fix. Users can check if the fix is installed in their devices by going to Settings>System>About Phone>Build Number. The build number should be “00WW_3_39B_SP03” or “00WW_3_22C_SP05“. If the build number does not match, users may need to update their device. This can be done by going to Settings> System> Advanced>System Update>Check for Update. Also Read:
Also Read: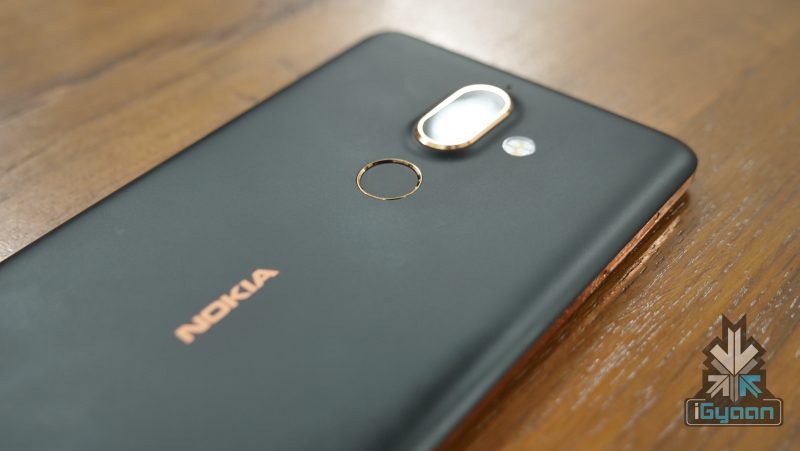 
 Reports state that sensitive data was being sent to a Chinese domain whenever the device was being switched on or being unlocked. The transferred data included the SIM card number, geographical location and the device’s serial number. Interestingly, the domain name of the Chinese server was vnet.cn, which refer to the China Internet Network Information Center, or CNNIC. The aforementioned domain is owned by the state-run Chinese Telecom operator.
Reports state that sensitive data was being sent to a Chinese domain whenever the device was being switched on or being unlocked. The transferred data included the SIM card number, geographical location and the device’s serial number. Interestingly, the domain name of the Chinese server was vnet.cn, which refer to the China Internet Network Information Center, or CNNIC. The aforementioned domain is owned by the state-run Chinese Telecom operator. Also Read:
Also Read: 
 Organizations usually encode user passwords with a process called hashing, which includes the
Organizations usually encode user passwords with a process called hashing, which includes the  Facebook’s VP stated that the flaw was detected as a part of a routine security review in the month of January. He also stated that Facebook’s login technology employs a different strategy that doesn’t risk the exposure of sensitive data. Also, he mentioned that the company had found no evidence of the data being accessed improperly and that the passwords were never visible to any person outside the organization. After being brought to light, the company itself came forward with a statement that it will notify all the Facebook and Instagram users regarding the bug, and how it has fixed all instances of the same.
Facebook’s VP stated that the flaw was detected as a part of a routine security review in the month of January. He also stated that Facebook’s login technology employs a different strategy that doesn’t risk the exposure of sensitive data. Also, he mentioned that the company had found no evidence of the data being accessed improperly and that the passwords were never visible to any person outside the organization. After being brought to light, the company itself came forward with a statement that it will notify all the Facebook and Instagram users regarding the bug, and how it has fixed all instances of the same.

 These days, smartphones are loaded with a host of security options to ensure that the data on the device remains private to the user. Some primary security features are listed below:
These days, smartphones are loaded with a host of security options to ensure that the data on the device remains private to the user. Some primary security features are listed below:
 The processor in the scanner module ensures that the image generated is clear enough to process. In addition, the processor also checks the pixel darkness. If the image is too dark or too light, it is discarded. The scanner then adjusts the exposure time of the sensor and scans the fingerprint again. As soon as a crisp image is generated, the fingerprint is cross checked with other images/prints of the finger. Every fingerprint signature is entirely unique, so any print that matches any other image in the list is picked as the verifiable one.
The processor in the scanner module ensures that the image generated is clear enough to process. In addition, the processor also checks the pixel darkness. If the image is too dark or too light, it is discarded. The scanner then adjusts the exposure time of the sensor and scans the fingerprint again. As soon as a crisp image is generated, the fingerprint is cross checked with other images/prints of the finger. Every fingerprint signature is entirely unique, so any print that matches any other image in the list is picked as the verifiable one. Unlike Digital Scanners, Capacitive scanners make use of electrical current to verify fingerprints. The capacitive sensors are made of semiconductor chips. Each chip contains a small array of cells with conductor plates, which in turn are covered by an insulating material. When the finger is placed on a capacitive scanner, the finger’s image is developed by the process of varying input and output voltage.
Unlike Digital Scanners, Capacitive scanners make use of electrical current to verify fingerprints. The capacitive sensors are made of semiconductor chips. Each chip contains a small array of cells with conductor plates, which in turn are covered by an insulating material. When the finger is placed on a capacitive scanner, the finger’s image is developed by the process of varying input and output voltage. Ultrasonic Scanners are fairly recent. Samsung’s latest
Ultrasonic Scanners are fairly recent. Samsung’s latest 
 Full fingerprints are extremely difficult to fake, but instead, the smartphone fingerprint scanners only record partial fingerprint signatures. Findings indicate that if a person creates a glove with a masterprint (with the highest possible number of ridge-and-valley combinations), he/she can break into a fingerprint protected device 40 to 50 percent of times before the smartphone asks for a numeric PIN. And that’s a scary high probability of something like this happening in our daily life, again, highly unlikely.
Full fingerprints are extremely difficult to fake, but instead, the smartphone fingerprint scanners only record partial fingerprint signatures. Findings indicate that if a person creates a glove with a masterprint (with the highest possible number of ridge-and-valley combinations), he/she can break into a fingerprint protected device 40 to 50 percent of times before the smartphone asks for a numeric PIN. And that’s a scary high probability of something like this happening in our daily life, again, highly unlikely.