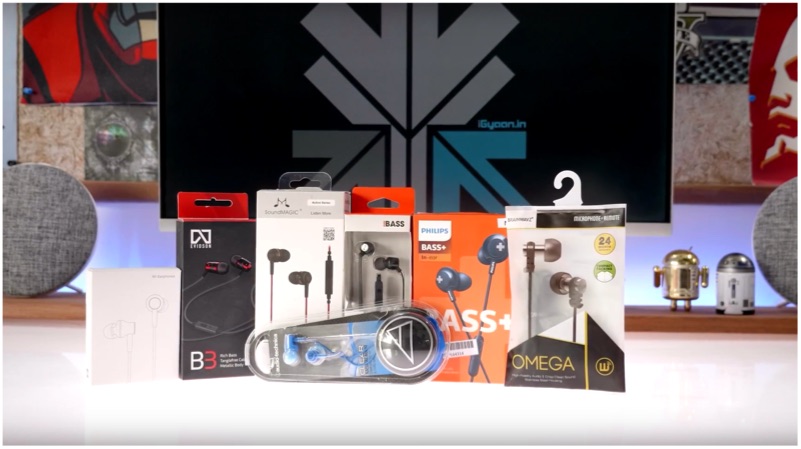
With the ever-increasing advancement in technology, smartphones have evolved in a lot of ways over the years. But despite all of that innovation, one function of it hasn’t always been up to the mark. That feature is the sound or to be more precise, their inbuilt speakers. While devices like the Apple iPhone XS, XS Max, XR, Samsung Galaxy S10 series and the Pixel 3/3XL offer stereo sound, there may always be a need for a more powerful, dedicated sound system. In selecting a good, portable wireless speaker, the options present in the market can be overwhelming. To make the choice easier, we have combined the best options under Rs. 2,000 available in the market currently.
Mi Basic 2
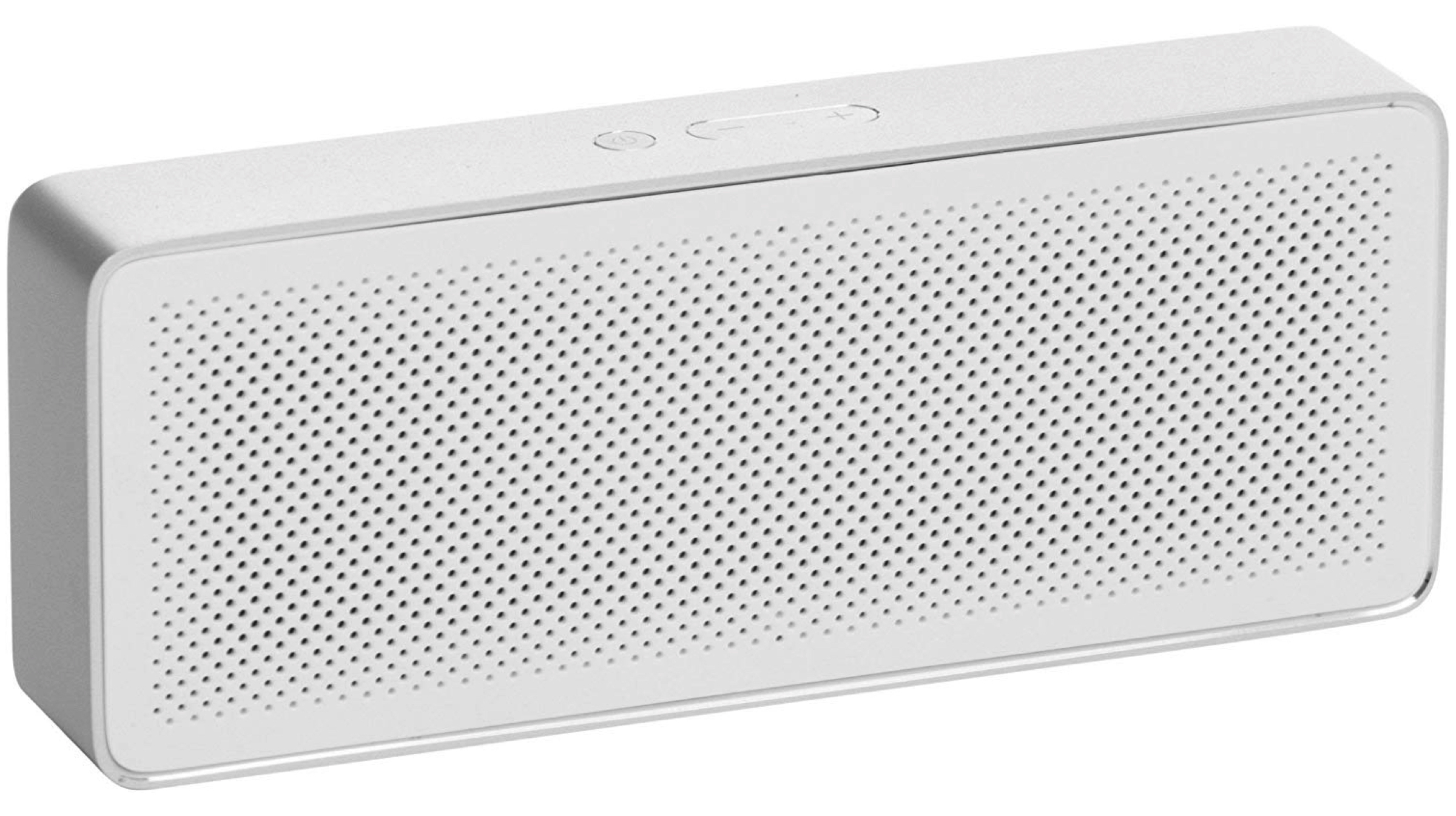

While talking about an affordable electronic device, it is quite inevitable to talk about Xiaomi. The Mi Basic 2 Bluetooth speaker is made out of aluminium frame and weighs 237g. Rated output of the drivers is 5W and the claimed battery life is 10 hours. With a great sound quality for the price, minimalistic looks and a portable design, the speakers are one of the best choices in the market currently.
JBL GO

The JBL GO is one of the most popular speakers under Rs. 2,000. It is also bolstered by the fact that it is available in eight different eye-popping colours and weighs a nimble 132g. The maximum output power of the speaker is 3W. While this is lower than what the competition offers, the JBL GO is more portable and has the brand name of an audio equipment giant to back them up. Due to the sheer portability and looks alone, the speakers are one of the best options in the price range.
Philips BT50B
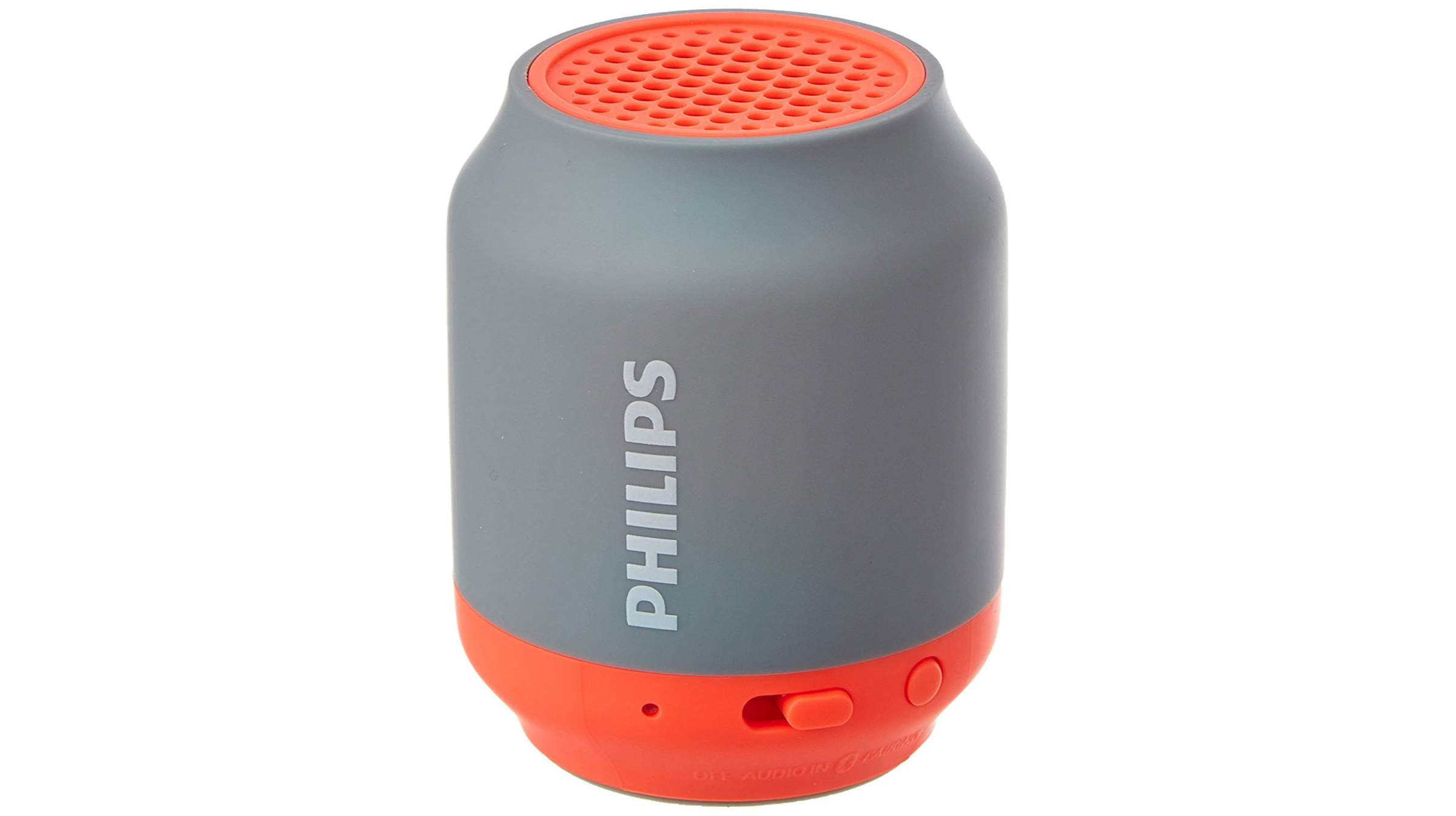

The Phillips BT50B is one of the most portable wireless speakers available in the market. Offered in four different colour variants, the sound output of the mono speaker is rated at 2W. While it doesn’t seem much on paper, it is a great sounding speaker when compared to its size. The rated battery life is 6 hours on a single charge and the weight of the speakers is a measly 90g. Also, the portability and a good sound output make it a great option in wireless speakers under the price of Rs. 2,000.
Boat Stone 650
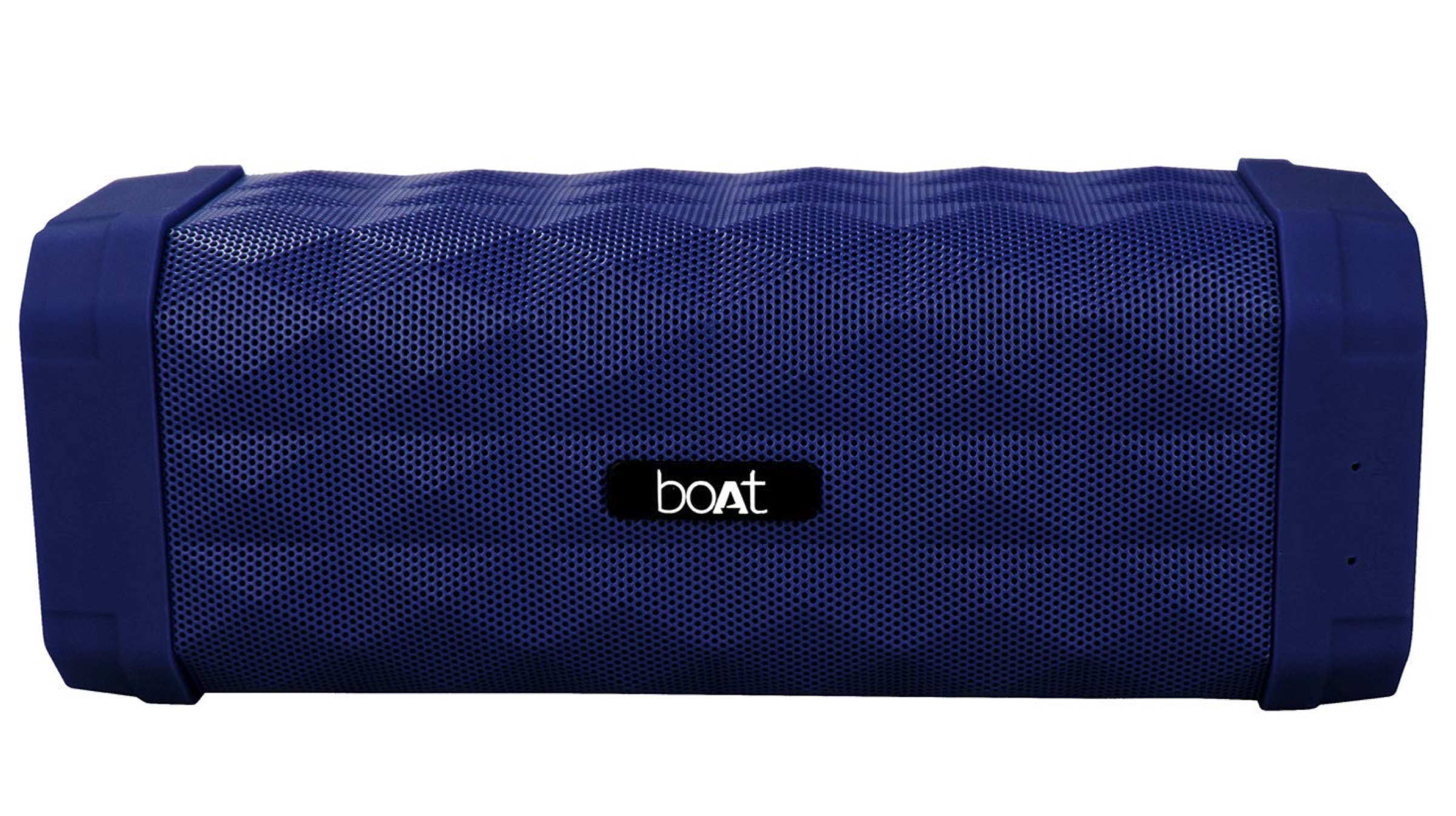

The company Boat is known to make quality audio accessories at an affordable price. The Stone 650 is no different. While not the most compact options, the Bluetooth speakers offer a rugged build and an IPX5 rating for water resistance. Sound output is rated at 10W with the help of a dual driver setup inside. Battery life is also good, as the speakers are rated to last 7 hours on a single charge. Despite its size, the speakers weigh 653g which makes them fairly portable. The mix of a great sound and a competitive price makes it one of the best options in the market.
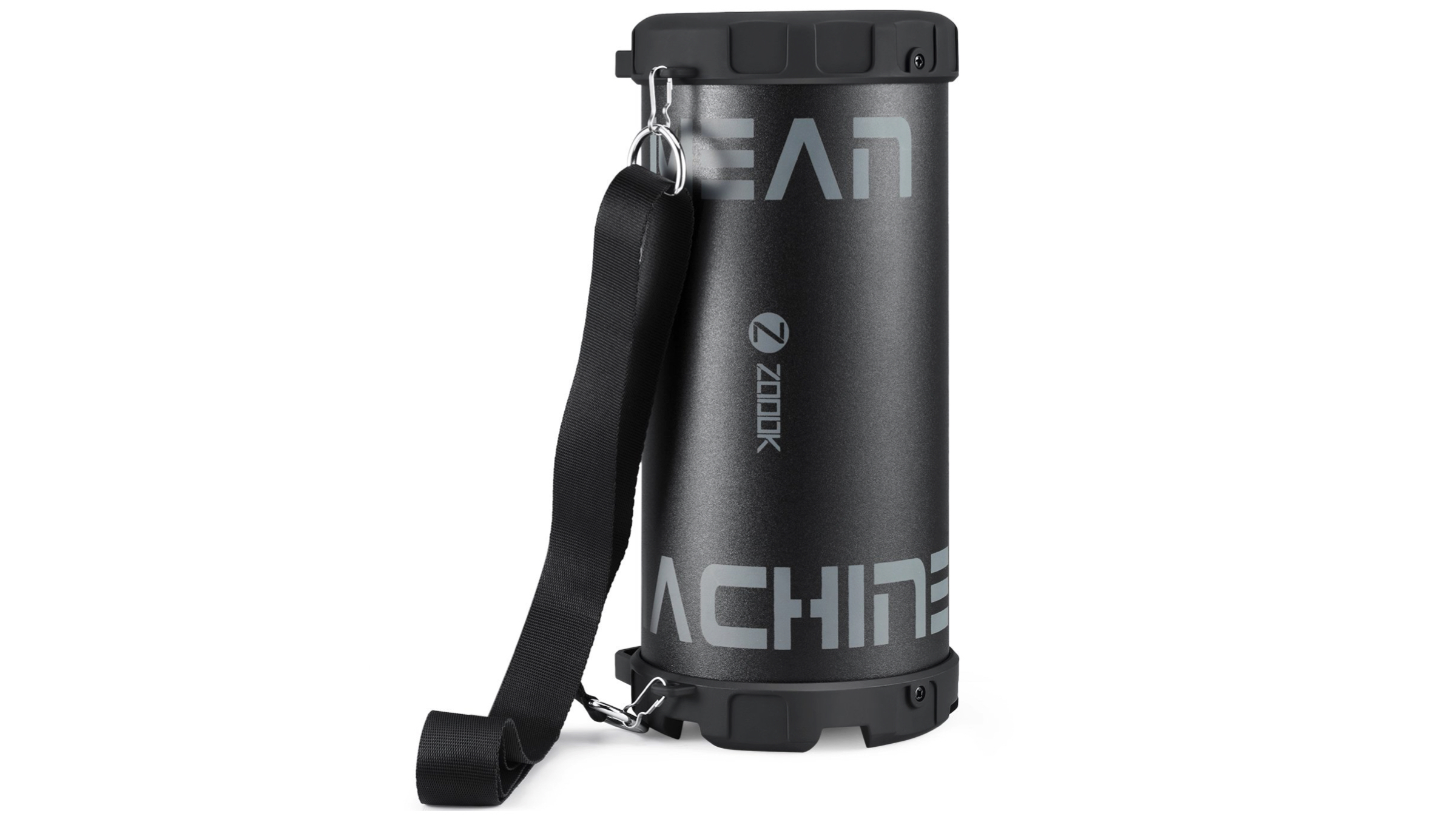
Zoook Rocker M2-Mean Machine

Also read: Steam Survey Shows The NVIDIA GTX 1060 As The Most Popular Graphics Card
The Bluetooth speakers justify its naming perfectly, with a rugged and cylindrical design. The Zook Rocker M2 have a barrage of ports and slots to play music and charge the device. It has a shoulder strap that is included in the box, which makes them fairly portable and easy o carry around. The rated sound output of 10W and a claimed battery life of 6 hours on a single charge make it one of the best sounding and the best options available under the price of Rs. 2,000.












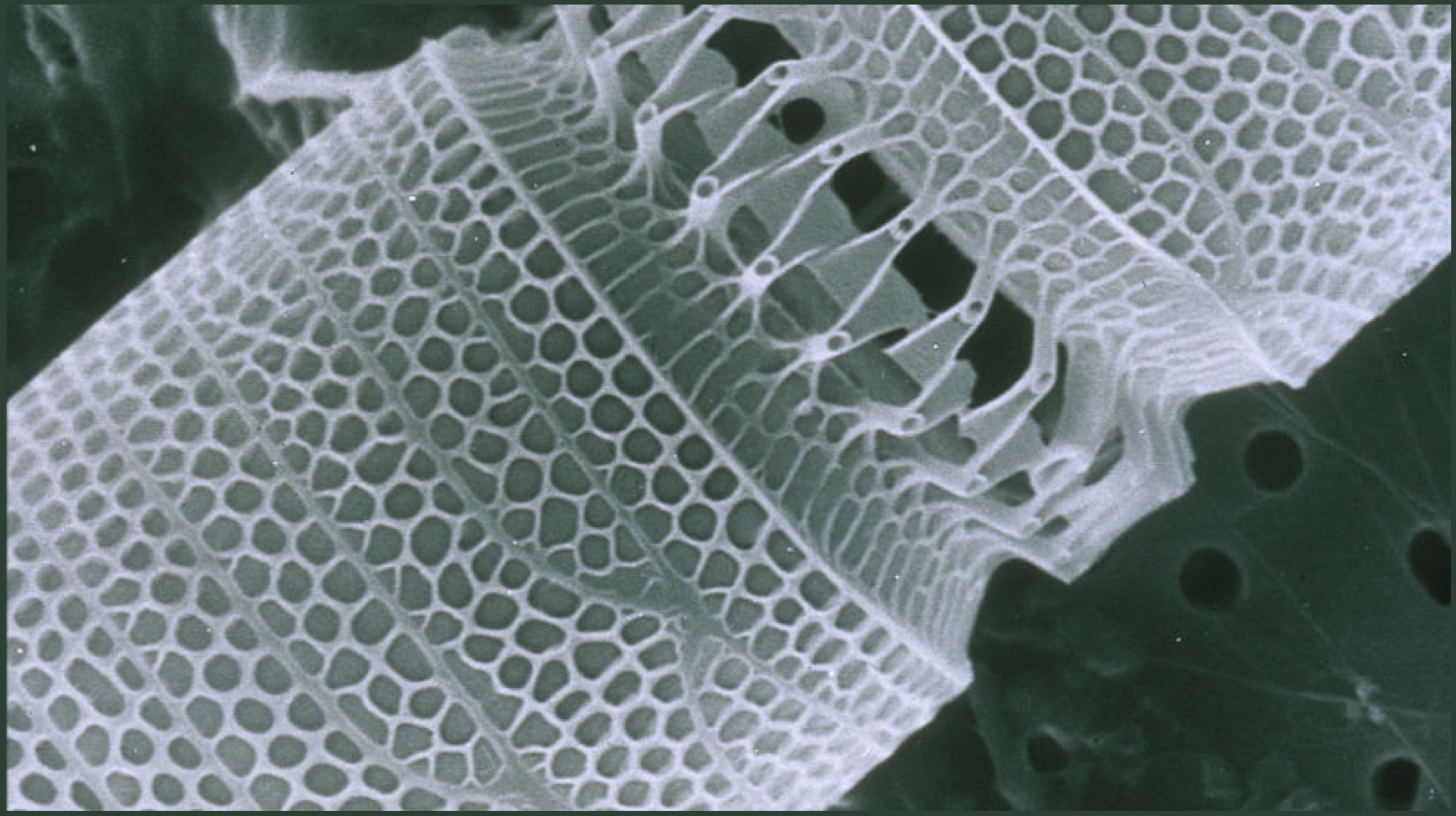
 Nanotechnology has been around for a while now. It is a branch of technology so minuscule that it can operate on a microscopic level. And what’s more, it can be programmed to do whatever is desired of it.
Nanotechnology has been around for a while now. It is a branch of technology so minuscule that it can operate on a microscopic level. And what’s more, it can be programmed to do whatever is desired of it. 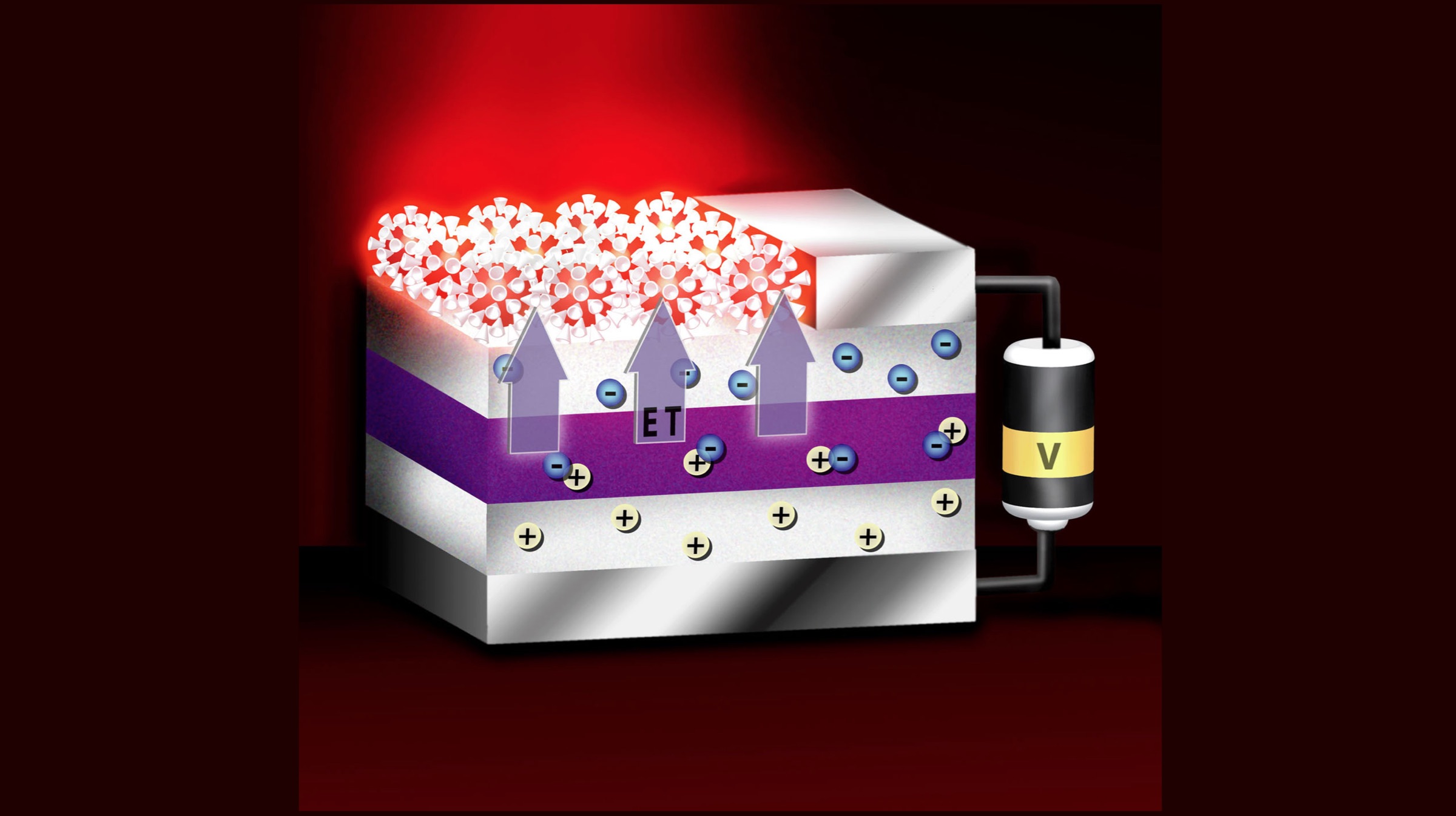
 In 2016, researchers used nanobots to treat a tumour by targeting it via nanobots, which then administered the necessary medicine to the clot of cells. This means that no surgery was involved to treat the tumour, no incisions were made and no anaesthesia was involved. It is very heart-warming to think that cancer may be a thing of the past in a decade or so. Chemotherapy and cancer treatments could be rendered obsolete for all we know.
In 2016, researchers used nanobots to treat a tumour by targeting it via nanobots, which then administered the necessary medicine to the clot of cells. This means that no surgery was involved to treat the tumour, no incisions were made and no anaesthesia was involved. It is very heart-warming to think that cancer may be a thing of the past in a decade or so. Chemotherapy and cancer treatments could be rendered obsolete for all we know.  Imagine that a person is unfortunately involved in a severe accident and is bleeding profusely, probably towards his/her death. Nanobots can heal up the damaged tissue right before your eyes. The microscopic robots are programmed to swarm like bats to scout out the point that needs repair. Once the point of activation is detected, all the bots collectively work together to fix it.
Imagine that a person is unfortunately involved in a severe accident and is bleeding profusely, probably towards his/her death. Nanobots can heal up the damaged tissue right before your eyes. The microscopic robots are programmed to swarm like bats to scout out the point that needs repair. Once the point of activation is detected, all the bots collectively work together to fix it. As per surveys, almost 41 percent of the total energy consumed in the United States is routed to construction and building. Nanotechnology can significantly reduce construction times and energy consumption that is involved in development. Deeper applications include maintenance of buildings, safety facilities and self-cleaning. Using micron-sized coatings, the nanoparticles can provide UV resistance in both coatings and paints. Nanoparticles of compounds like Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide can be applied as a final layer on construction ceramics to provide the aforementioned resistance.
As per surveys, almost 41 percent of the total energy consumed in the United States is routed to construction and building. Nanotechnology can significantly reduce construction times and energy consumption that is involved in development. Deeper applications include maintenance of buildings, safety facilities and self-cleaning. Using micron-sized coatings, the nanoparticles can provide UV resistance in both coatings and paints. Nanoparticles of compounds like Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide can be applied as a final layer on construction ceramics to provide the aforementioned resistance. In the last 13 years, the Indian Army lost a soldier on duty every third day. Casualties on the front line are much higher in number than in any other profession. The development of nanobots in the Military sector will ensure that the number of lives lost is drastically reduced. For starters, nanorobots can be used to scout the front lines for any impending risks. They can be used for spying and scouring sensitive information without putting any human lives at risk.
In the last 13 years, the Indian Army lost a soldier on duty every third day. Casualties on the front line are much higher in number than in any other profession. The development of nanobots in the Military sector will ensure that the number of lives lost is drastically reduced. For starters, nanorobots can be used to scout the front lines for any impending risks. They can be used for spying and scouring sensitive information without putting any human lives at risk. Kevlar vests can be designed with nanoparticles to provide material regeneration during combat. Weapons developed with nanoparticles will be lighter and more modular than conventional weapons. Military nanorobots will be capable of performing complex functions like grabbing and wielding heavy objects, which can be used to safely neutralize threats like IEDs and Mines.
Kevlar vests can be designed with nanoparticles to provide material regeneration during combat. Weapons developed with nanoparticles will be lighter and more modular than conventional weapons. Military nanorobots will be capable of performing complex functions like grabbing and wielding heavy objects, which can be used to safely neutralize threats like IEDs and Mines.
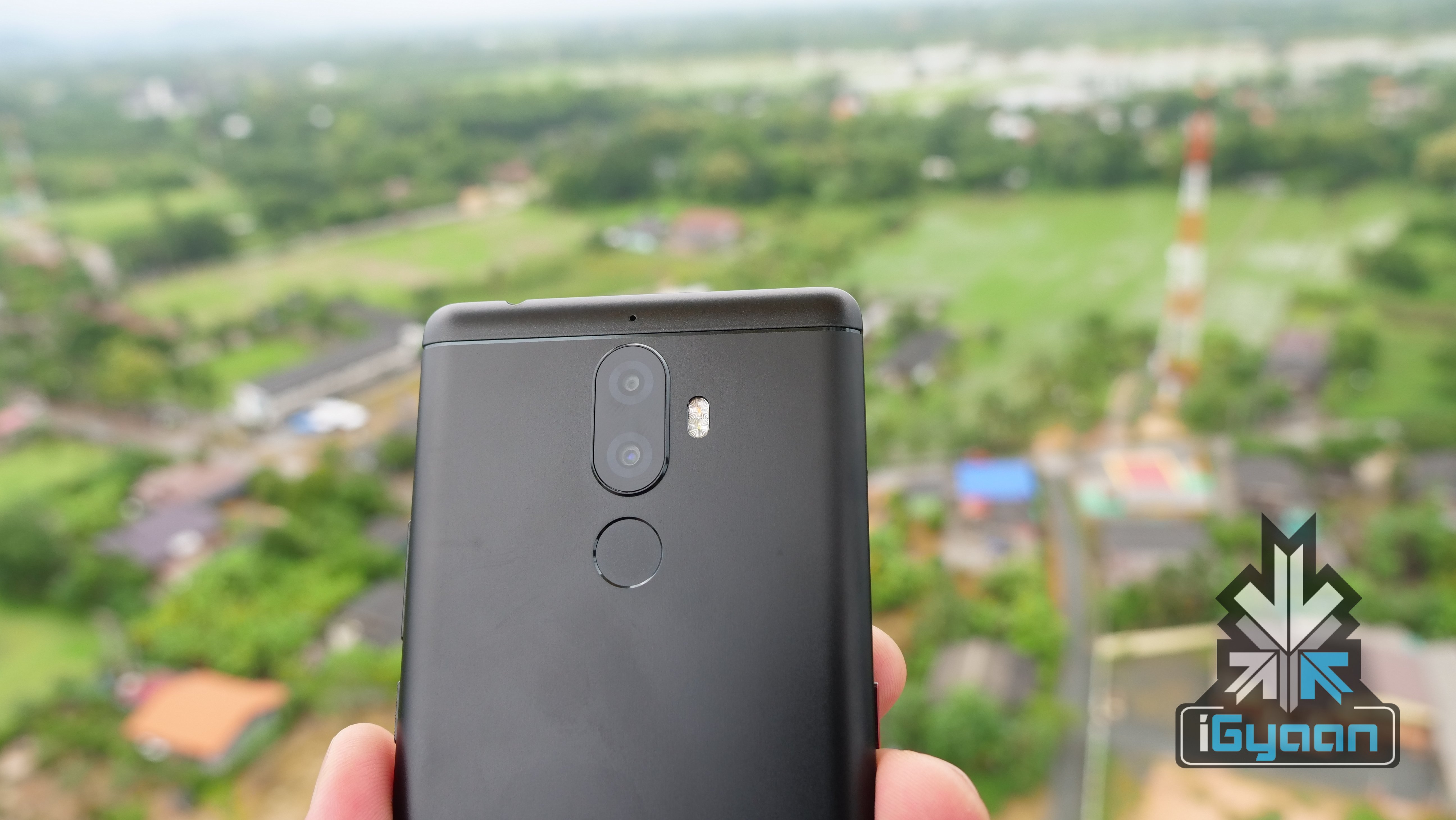 These days, smartphones are loaded with a host of security options to ensure that the data on the device remains private to the user. Some primary security features are listed below:
These days, smartphones are loaded with a host of security options to ensure that the data on the device remains private to the user. Some primary security features are listed below: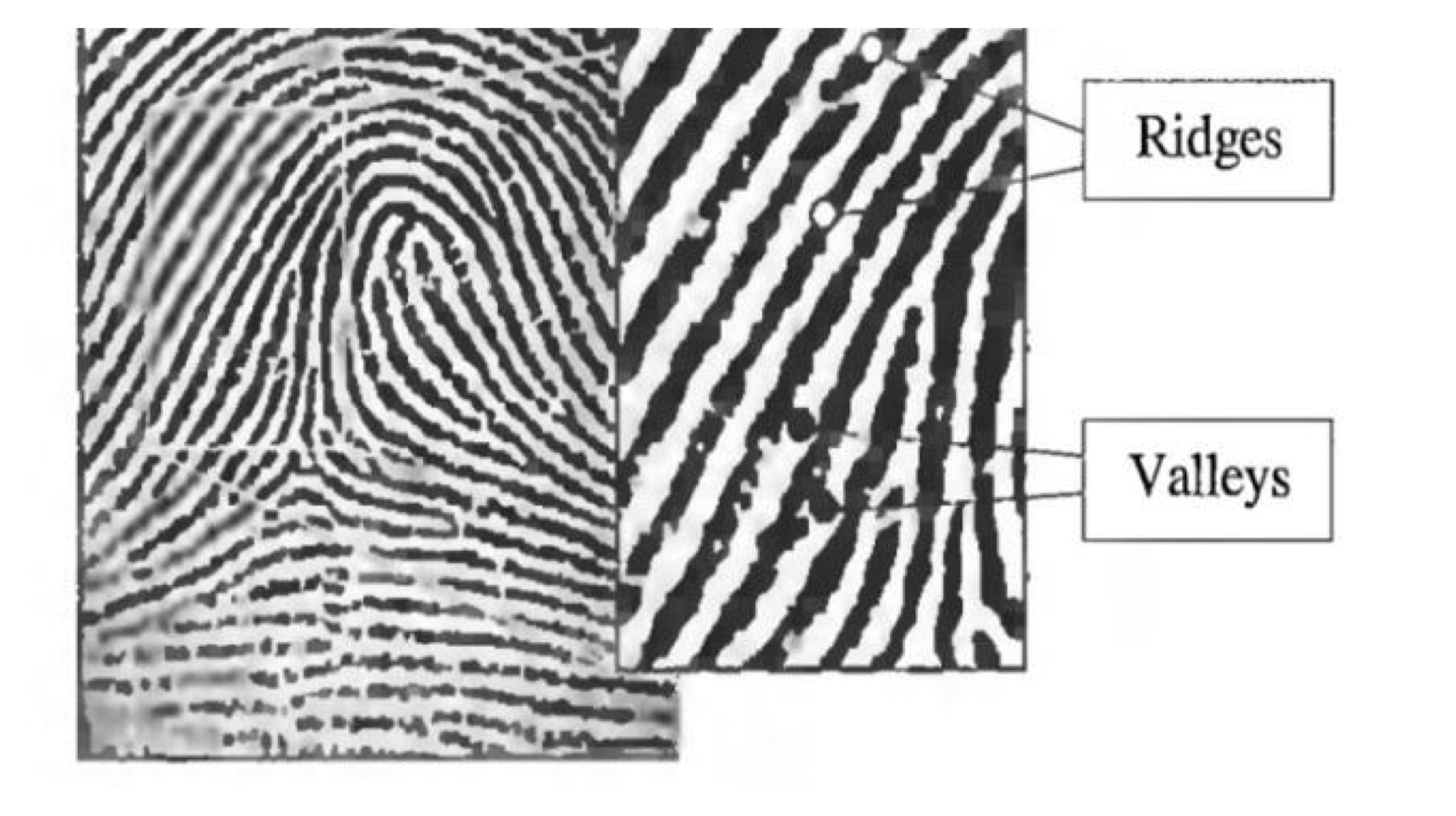
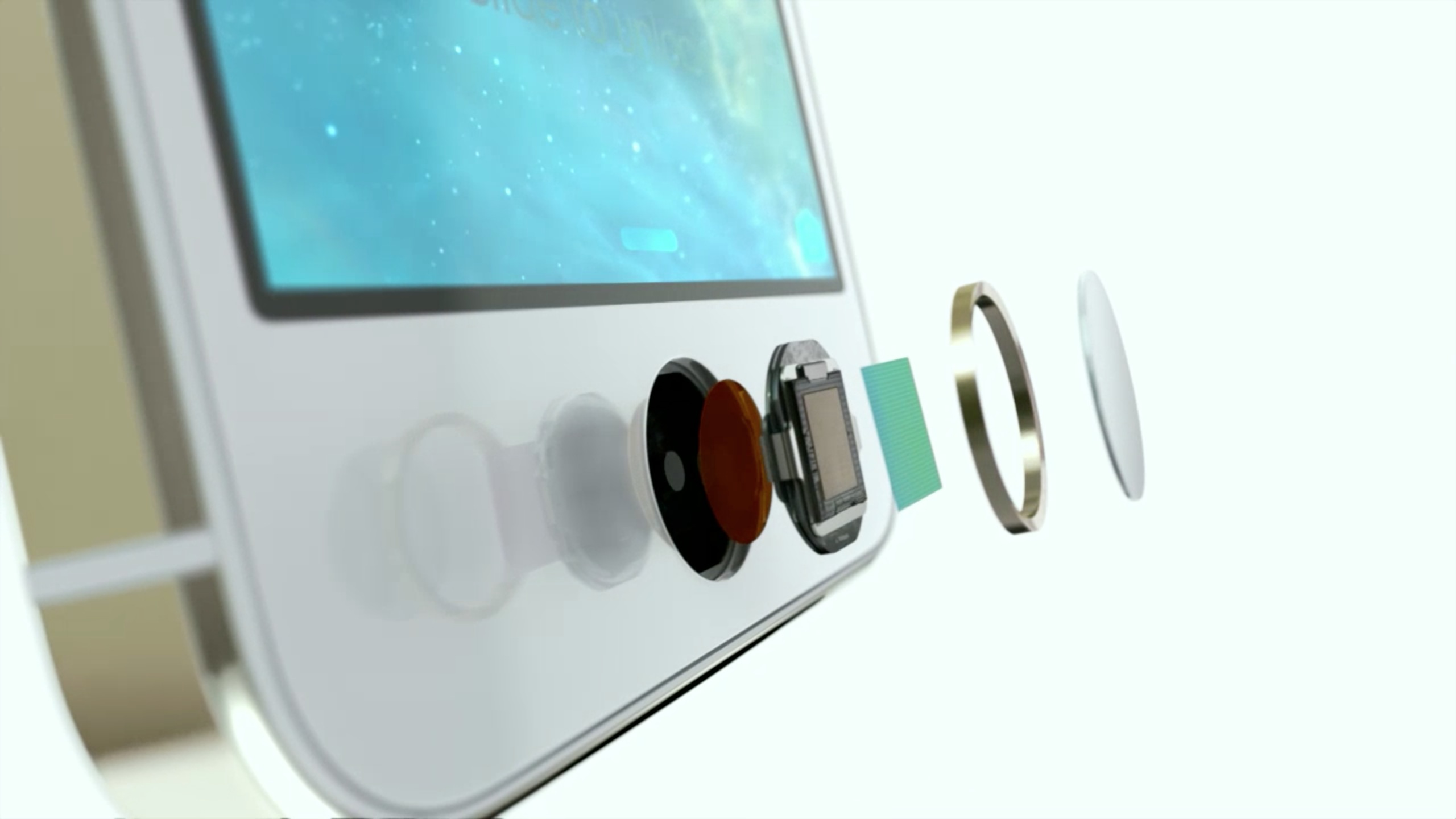 The processor in the scanner module ensures that the image generated is clear enough to process. In addition, the processor also checks the pixel darkness. If the image is too dark or too light, it is discarded. The scanner then adjusts the exposure time of the sensor and scans the fingerprint again. As soon as a crisp image is generated, the fingerprint is cross checked with other images/prints of the finger. Every fingerprint signature is entirely unique, so any print that matches any other image in the list is picked as the verifiable one.
The processor in the scanner module ensures that the image generated is clear enough to process. In addition, the processor also checks the pixel darkness. If the image is too dark or too light, it is discarded. The scanner then adjusts the exposure time of the sensor and scans the fingerprint again. As soon as a crisp image is generated, the fingerprint is cross checked with other images/prints of the finger. Every fingerprint signature is entirely unique, so any print that matches any other image in the list is picked as the verifiable one.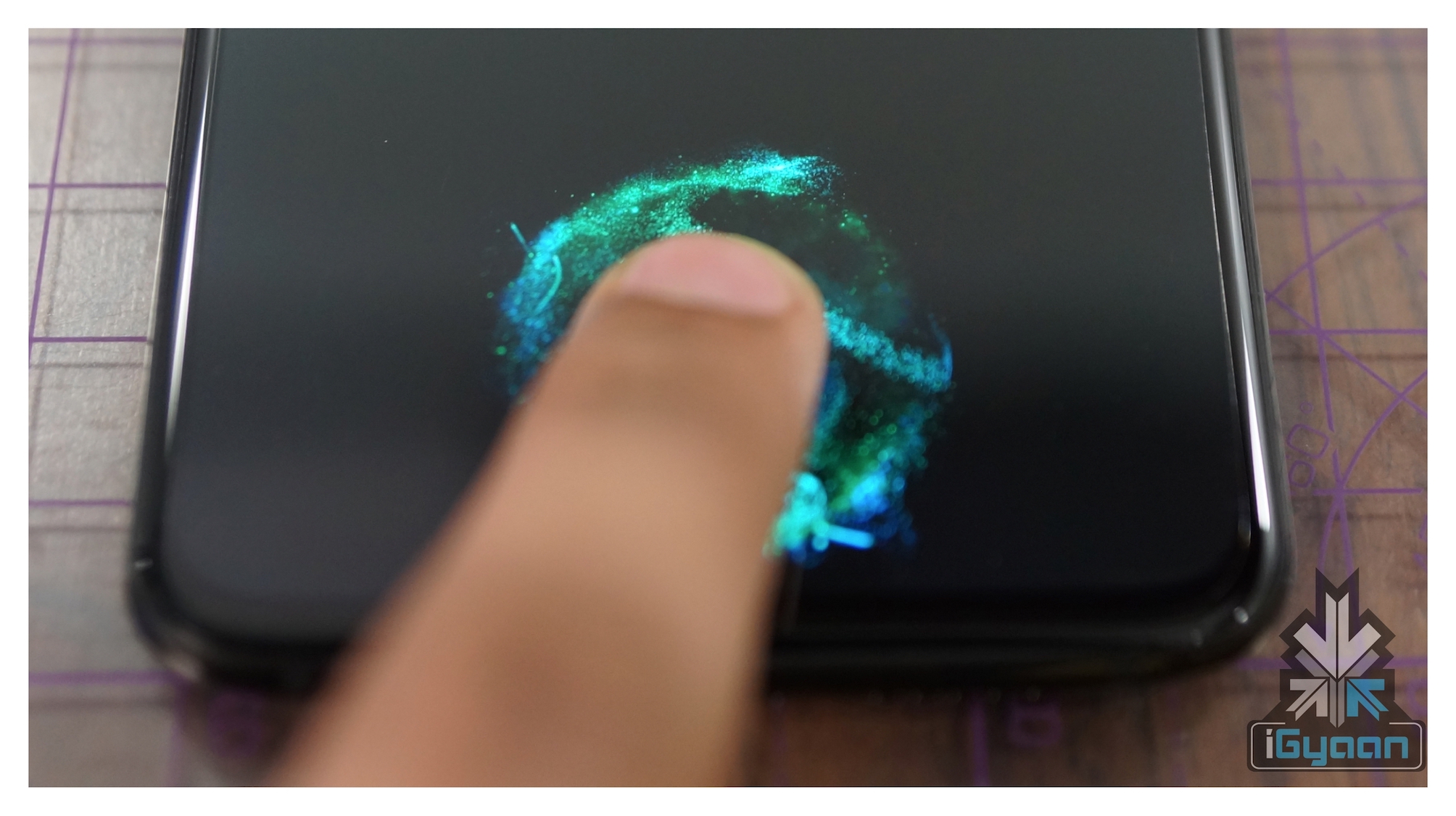 Unlike Digital Scanners, Capacitive scanners make use of electrical current to verify fingerprints. The capacitive sensors are made of semiconductor chips. Each chip contains a small array of cells with conductor plates, which in turn are covered by an insulating material. When the finger is placed on a capacitive scanner, the finger’s image is developed by the process of varying input and output voltage.
Unlike Digital Scanners, Capacitive scanners make use of electrical current to verify fingerprints. The capacitive sensors are made of semiconductor chips. Each chip contains a small array of cells with conductor plates, which in turn are covered by an insulating material. When the finger is placed on a capacitive scanner, the finger’s image is developed by the process of varying input and output voltage.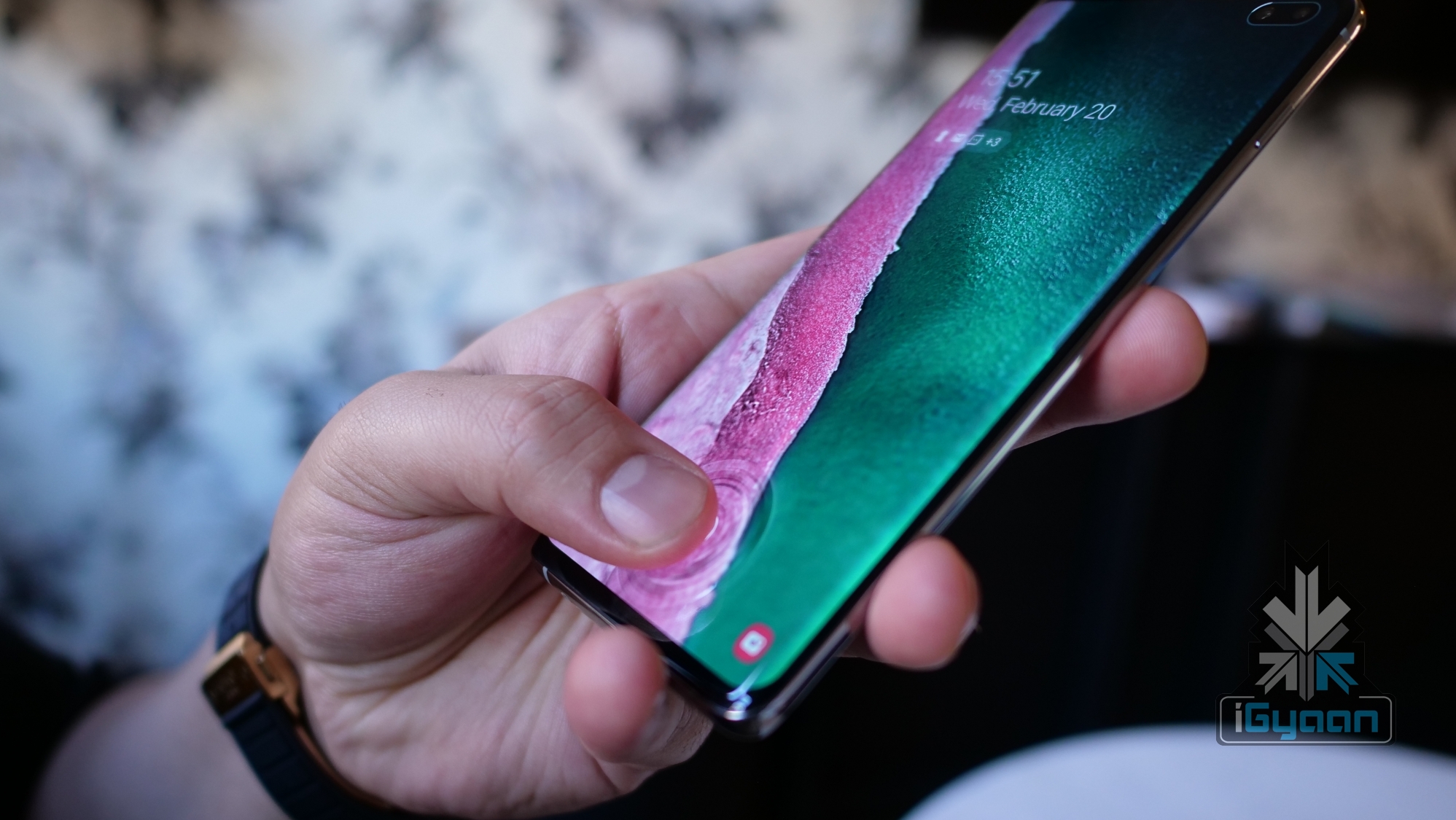 Ultrasonic Scanners are fairly recent. Samsung’s latest
Ultrasonic Scanners are fairly recent. Samsung’s latest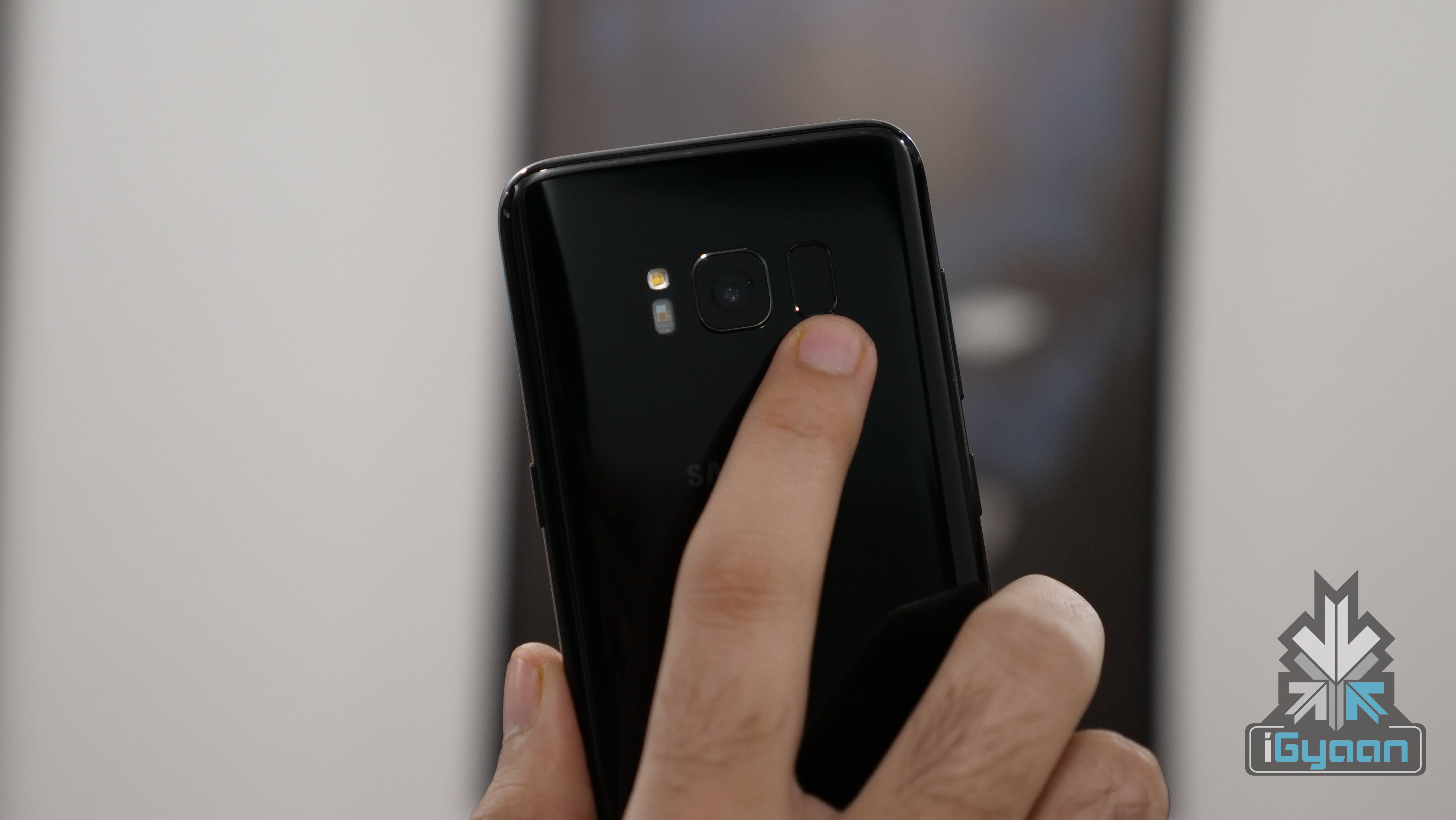 
 Full fingerprints are extremely difficult to fake, but instead, the smartphone fingerprint scanners only record partial fingerprint signatures. Findings indicate that if a person creates a glove with a masterprint (with the highest possible number of ridge-and-valley combinations), he/she can break into a fingerprint protected device 40 to 50 percent of times before the smartphone asks for a numeric PIN. And that’s a scary high probability of something like this happening in our daily life, again, highly unlikely.
Full fingerprints are extremely difficult to fake, but instead, the smartphone fingerprint scanners only record partial fingerprint signatures. Findings indicate that if a person creates a glove with a masterprint (with the highest possible number of ridge-and-valley combinations), he/she can break into a fingerprint protected device 40 to 50 percent of times before the smartphone asks for a numeric PIN. And that’s a scary high probability of something like this happening in our daily life, again, highly unlikely.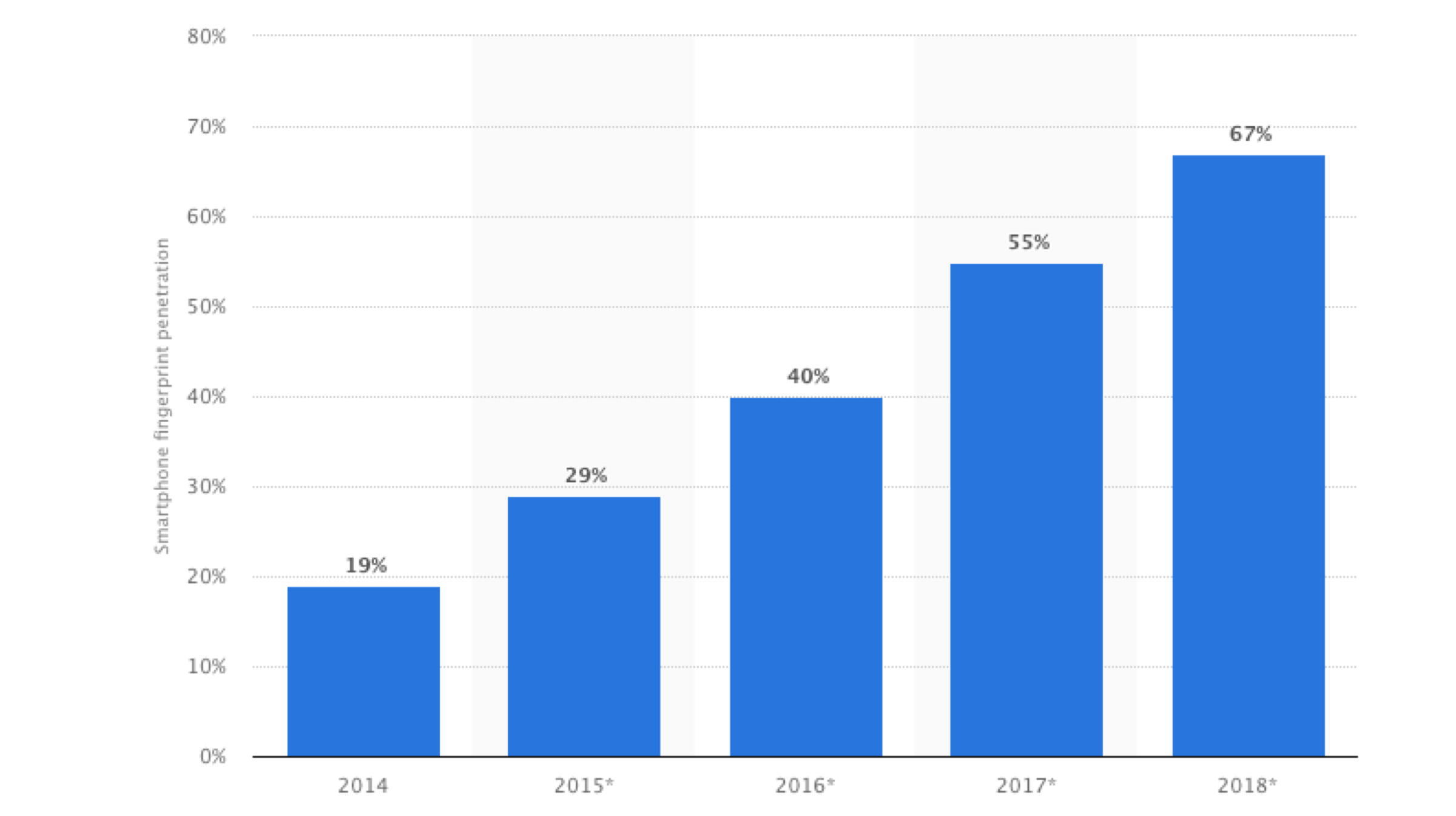











 Music applications like Apple Music and Last.fm have been around for a long time too. There are still a lot of users who side with apps like Saavn, Gaana and Soundcloud. But the reason why Spotify is different are the algorithms that form the basis of what the service is. Over 100 million users use Spotify’s music algorithm every month to listen to music that’s tailored for them. An Indie music fan wouldn’t be a huge fan of Electronic Music, and someone who likes Hip hop would not exactly enjoy folk music.
Music applications like Apple Music and Last.fm have been around for a long time too. There are still a lot of users who side with apps like Saavn, Gaana and Soundcloud. But the reason why Spotify is different are the algorithms that form the basis of what the service is. Over 100 million users use Spotify’s music algorithm every month to listen to music that’s tailored for them. An Indie music fan wouldn’t be a huge fan of Electronic Music, and someone who likes Hip hop would not exactly enjoy folk music. Spotify understands that. In 2015, the company launched its ‘Discover Weekly’ feature, which allowed users to explore a weekly playlist that’s curated by Spotify. The playlist includes soundtracks that the user might like, based on his/her listening history. Not just that, the algorithm also goes through the most recent releases for each artist you like, runs it through a user base of almost 2 billion similar playlists and adds that music to your playlist. Usually, people get used to listening to the same songs every day, but Spotify users have reported that the “Discover Weekly” feature makes listening to music a lot more fun than ever. It’s like the algorithm personally knows its users, listeners state.
Spotify understands that. In 2015, the company launched its ‘Discover Weekly’ feature, which allowed users to explore a weekly playlist that’s curated by Spotify. The playlist includes soundtracks that the user might like, based on his/her listening history. Not just that, the algorithm also goes through the most recent releases for each artist you like, runs it through a user base of almost 2 billion similar playlists and adds that music to your playlist. Usually, people get used to listening to the same songs every day, but Spotify users have reported that the “Discover Weekly” feature makes listening to music a lot more fun than ever. It’s like the algorithm personally knows its users, listeners state.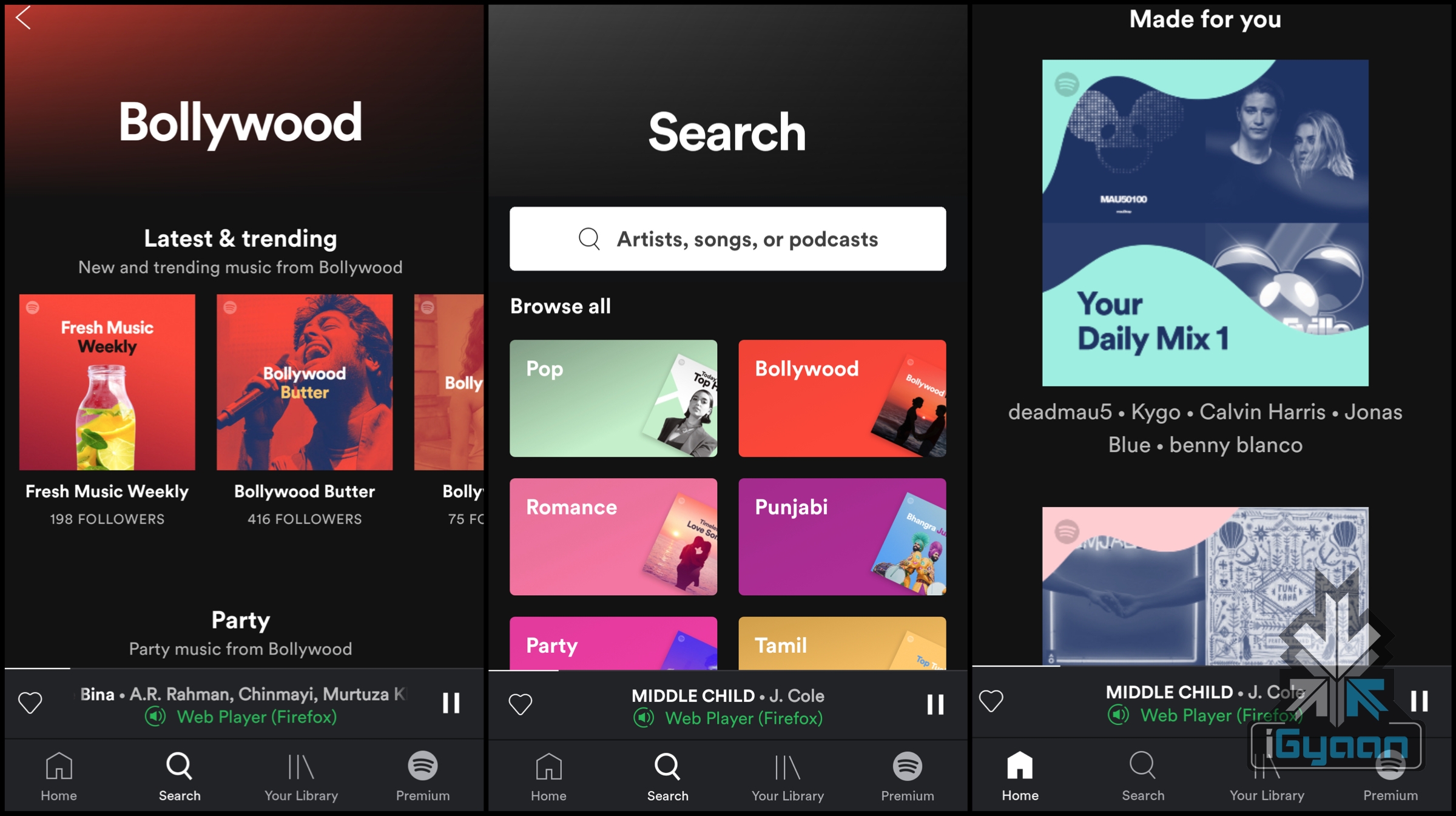 To make it simpler, one of the first media streaming services that used this algorithm was Netflix. It analyzed a user’s rating for a specific movie and compared it with another user’s rating to find out which movie taste such users had in common. After that, it used this analysis to recommend movies to similar users. Needless to say, Netflix was hugely successful, because it “knew” what people liked and how to keep an audience hooked.
To make it simpler, one of the first media streaming services that used this algorithm was Netflix. It analyzed a user’s rating for a specific movie and compared it with another user’s rating to find out which movie taste such users had in common. After that, it used this analysis to recommend movies to similar users. Needless to say, Netflix was hugely successful, because it “knew” what people liked and how to keep an audience hooked. Natural language processing (NLP) is a technique that has long been used for translating human speech to machine language. A lot of websites other than Spotify use NLP to find related text across different websites, acting upon which they can implement that newfound information on their own platform. NLP holds a very high spot in the list of algorithms that are used for mining big data.
Natural language processing (NLP) is a technique that has long been used for translating human speech to machine language. A lot of websites other than Spotify use NLP to find related text across different websites, acting upon which they can implement that newfound information on their own platform. NLP holds a very high spot in the list of algorithms that are used for mining big data. Analyzing Raw audio models is basically Spotify’s way to ensure that new tracks don’t go unnoticed. Take it this way – taking a technology similar to Facial Recognition and applying it to soundtracks is what Spotify does. It analyzes the audio data including the wavelength, time signatures, key, tempo and loudness of a music track, and then uses the same to find more tracks with similar audio signatures. This allows the music service to detect similarities between songs and therefore, it suggests those tracks to users.
Analyzing Raw audio models is basically Spotify’s way to ensure that new tracks don’t go unnoticed. Take it this way – taking a technology similar to Facial Recognition and applying it to soundtracks is what Spotify does. It analyzes the audio data including the wavelength, time signatures, key, tempo and loudness of a music track, and then uses the same to find more tracks with similar audio signatures. This allows the music service to detect similarities between songs and therefore, it suggests those tracks to users. Also Read:
Also Read: 
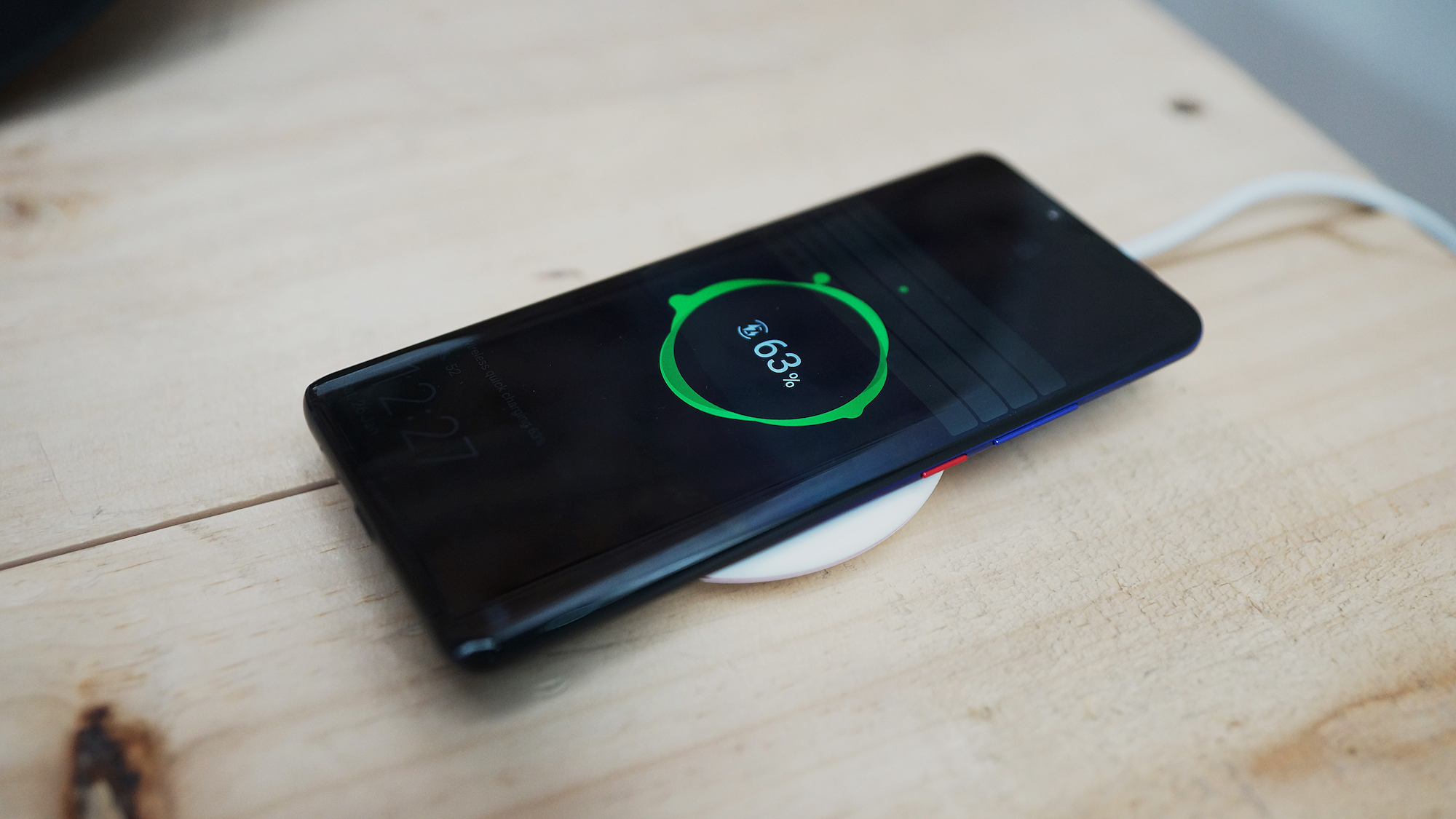

























 However, it is possible that the smartphone count may plummet sharply. Not because people will stop using smartphones. Because alternatives to smartphones are taking over the world. Wearables. This upcoming generation of technology could dethrone smartphones, once and for all. Wearables are defined as an electronic gadget that can be worn/clipped on the body. It’s a vast category, but the most common ones are
However, it is possible that the smartphone count may plummet sharply. Not because people will stop using smartphones. Because alternatives to smartphones are taking over the world. Wearables. This upcoming generation of technology could dethrone smartphones, once and for all. Wearables are defined as an electronic gadget that can be worn/clipped on the body. It’s a vast category, but the most common ones are As per a survey, over 51 percent of the youth uses some form of a fitness tracker to monitor daily health and activities. Smartwatch sales are booming day by day, clearly showcasing the fact that people are looking towards making their lives easier and faster-paced to catch up with the rest of the world. Hence, in a world where winning matters to a significantly larger chunk of the population, smartphones are slowing them down while speeding things up at the same time.
As per a survey, over 51 percent of the youth uses some form of a fitness tracker to monitor daily health and activities. Smartwatch sales are booming day by day, clearly showcasing the fact that people are looking towards making their lives easier and faster-paced to catch up with the rest of the world. Hence, in a world where winning matters to a significantly larger chunk of the population, smartphones are slowing them down while speeding things up at the same time. What makes a smartphone so special? Is it the CPU of the device? Or is it the fact that you can make calls via your smartphone? You can listen to music whenever you want, view pictures, get directions to a place you’re going to, or simply tell your smartphone voice assistant to book a taxi while you read an e-book.
What makes a smartphone so special? Is it the CPU of the device? Or is it the fact that you can make calls via your smartphone? You can listen to music whenever you want, view pictures, get directions to a place you’re going to, or simply tell your smartphone voice assistant to book a taxi while you read an e-book. In the not-so-distant future, a combination of swanky sunglasses/spectacles and a pair of earbuds will be able to do all of the aforementioned tasks, and so much more. A lot of companies are working on smart earbuds that will contain CPUs as powerful as smartphone processors and more efficient than them too. For instance, Here One earbuds from Doppler Labs have a feature that allows you to filter out what you hear. You’re probably thinking, “Hey, I heard about this feature some time back, didn’t I?” Well, these earbuds allow you to filter out selective sounds from your environment, like the crying of a baby, a person playing the piano or just some old fashioned crowd chatter. It wouldn’t be wrong to say that these earbuds are more powerful than some of the early computers. Sadly, the company stopped producing the earbuds because of the lack of funding.
In the not-so-distant future, a combination of swanky sunglasses/spectacles and a pair of earbuds will be able to do all of the aforementioned tasks, and so much more. A lot of companies are working on smart earbuds that will contain CPUs as powerful as smartphone processors and more efficient than them too. For instance, Here One earbuds from Doppler Labs have a feature that allows you to filter out what you hear. You’re probably thinking, “Hey, I heard about this feature some time back, didn’t I?” Well, these earbuds allow you to filter out selective sounds from your environment, like the crying of a baby, a person playing the piano or just some old fashioned crowd chatter. It wouldn’t be wrong to say that these earbuds are more powerful than some of the early computers. Sadly, the company stopped producing the earbuds because of the lack of funding. Just like adaptive filtering, a lot of other technologies are being implemented in wearables which can make a huge difference in the way we live our life. Motion sensing earbuds turn on when a user inserts them in his/her ears. Smartwatches detect almost every activity of the wearer, analyze them with the help of the chipset present on the device and provide analytics regarding the same. Wearable cameras click an image every time a catchphrase is detected or when a special gesture is recorded.
Just like adaptive filtering, a lot of other technologies are being implemented in wearables which can make a huge difference in the way we live our life. Motion sensing earbuds turn on when a user inserts them in his/her ears. Smartwatches detect almost every activity of the wearer, analyze them with the help of the chipset present on the device and provide analytics regarding the same. Wearable cameras click an image every time a catchphrase is detected or when a special gesture is recorded. With technology reaching a point where all the components of a device can be placed on a chipset which measures smaller than a fingernail, possibilities are endless. Projects like
With technology reaching a point where all the components of a device can be placed on a chipset which measures smaller than a fingernail, possibilities are endless. Projects like  Also Read:
Also Read: 








